Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
The World Portal
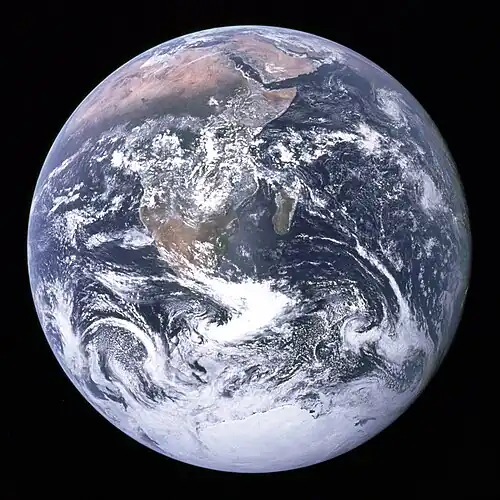
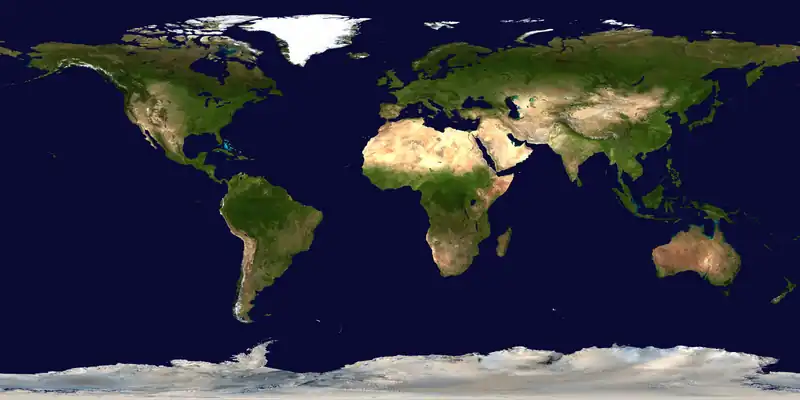

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology the world or universe is commonly defined as "[t]he totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole or world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy" or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles -
 Image 1Post-Kyoto negotiations refers to high level talks attempting to address global warming by limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Generally part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), these talks concern the period after the first "commitment period" of the Kyoto Protocol, which expired at the end of 2012. Negotiations have been mandated by the adoption of the Bali Road Map and Decision 1/CP.13 ("The Bali Action Plan").
Image 1Post-Kyoto negotiations refers to high level talks attempting to address global warming by limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Generally part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), these talks concern the period after the first "commitment period" of the Kyoto Protocol, which expired at the end of 2012. Negotiations have been mandated by the adoption of the Bali Road Map and Decision 1/CP.13 ("The Bali Action Plan").
UNFCCC negotiations are conducted within two subsidiary bodies, the Ad Hoc Working Group on Long-term Cooperative Action under the Convention (AWG-LCA) and the Ad Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP) and were expected to culminate in the United Nations Climate Change Conference taking place in December 2009 in Copenhagen (COP-15); negotiations are supported by a number of external processes, including the G8 process, a number of regional meetings and the Major Economies Forum on Energy and Climate that was launched by US President Barack Obama in March 2009. High level talks were held at the meeting of the G8+5 Climate Change Dialogue in February 2007 and at a number of subsequent G8 meetings, most recently leading to the adoption of the G8 leaders declaration "Responsible Leadership for a Sustainable Future" during the G8 summit in L´Aquila, Italy, in July 2009. (Full article...)![Image 2Dorothea Lange's Migrant Mother depicts destitute pea pickers in California, centering on Florence Owens Thompson, age 32, a mother of seven children, in Nipomo, California, March 1936.The Great Depression (1929–1939) was an economic shock that affected most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September 1929 and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of 24 October (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century.Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries,[specify] the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and in some countries rose as high as 33%. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 2The Great Depression (1929–1939) was an economic shock that affected most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September 1929 and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of 24 October (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century.
Image 2The Great Depression (1929–1939) was an economic shock that affected most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September 1929 and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of 24 October (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Dorothea Lange's Migrant Mother depicts destitute pea pickers in California, centering on Florence Owens Thompson, age 32, a mother of seven children, in Nipomo, California, March 1936.
Dorothea Lange's Migrant Mother depicts destitute pea pickers in California, centering on Florence Owens Thompson, age 32, a mother of seven children, in Nipomo, California, March 1936.
Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and in some countries rose as high as 33%. (Full article...) Image 3
Image 3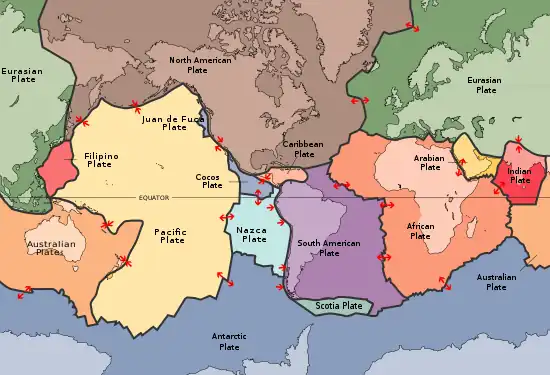 Plates in the crust of Earth
Plates in the crust of Earth
Earth's crust is Earth's thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates whose motion allows heat to escape the interior of the Earth into space.
The crust lies on top of the mantle, a configuration that is stable because the upper mantle is made of peridotite and is therefore significantly denser than the crust. The boundary between the crust and mantle is conventionally placed at the Mohorovičić discontinuity, a boundary defined by a contrast in seismic velocity. (Full article...) Image 4
Image 4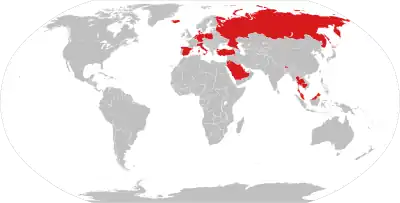 A map of nations which have Lèse-majesté laws as of September 2022
A map of nations which have Lèse-majesté laws as of September 2022
Freedom of speech is the concept of the inherent human right to voice one's opinion publicly without fear of government censorship or punishment. "Speech" is not limited to public speaking and is generally taken to include other forms of expression. The right is preserved in the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights and is granted formal recognition by the laws of most nations. Nonetheless, the degree to which the right is upheld in practice varies greatly from one nation to another. In many nations, particularly those with authoritarian forms of government, overt government censorship is enforced. Censorship has also been claimed to occur in other forms and there are different approaches to issues such as hate speech, obscenity, and defamation laws.
The following list is partially composed of the respective countries' government claims and does not fully reflect the de facto situation, however many sections of the page do contain information about the validity of the government's claims alongside said claims. (Full article...) Image 5The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many cultures that is present in Proto-Indo-European culture and other cultures and civilizations. Typically, the world egg is a beginning of some sort, and the universe or some primordial being comes into existence by "hatching" from the egg, sometimes lain on the primordial waters of the Earth.
Image 5The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many cultures that is present in Proto-Indo-European culture and other cultures and civilizations. Typically, the world egg is a beginning of some sort, and the universe or some primordial being comes into existence by "hatching" from the egg, sometimes lain on the primordial waters of the Earth.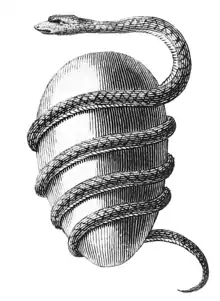 Jacob Bryant's Orphic Egg (1774)
Jacob Bryant's Orphic Egg (1774)
The modern cosmological versions of this idea are called the emergent Universe scenarios. (Full article...) Image 6The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.
Image 6The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.
The origins of the Internet date back to research to enable time-sharing of computer resources and the development of packet switching in the 1960s. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated a sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the network. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, subsequent commercialization is what incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Image 7
Image 7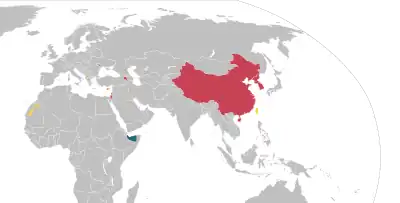 Non-UN member states recognised by at least one UN member stateNon-UN member states recognised only by other non-UN member states
Non-UN member states recognised by at least one UN member stateNon-UN member states recognised only by other non-UN member states
A number of polities have declared independence and sought diplomatic recognition from the international community as sovereign states, but have not been universally recognised as such. These entities often have de facto control of their territory. A number of such entities have existed in the past.
There are two traditional theories used to indicate how a sovereign state comes into being. The declarative theory (codified in the 1933 Montevideo Convention) defines a state as a person in international law if it meets the following criteria: (Full article...)
General images -
 Image 1A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
Image 1A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth).jpg.webp)

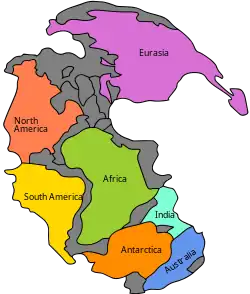 Image 4Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
Image 4Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth).jpg.webp) Image 5Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
Image 5Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
 Image 7Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
Image 7Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth) Image 8Japanese depiction of Portuguese trading carrack. Shipbuilding advances in Late Middle Ages led to global European presence in the early modern period.
Image 8Japanese depiction of Portuguese trading carrack. Shipbuilding advances in Late Middle Ages led to global European presence in the early modern period.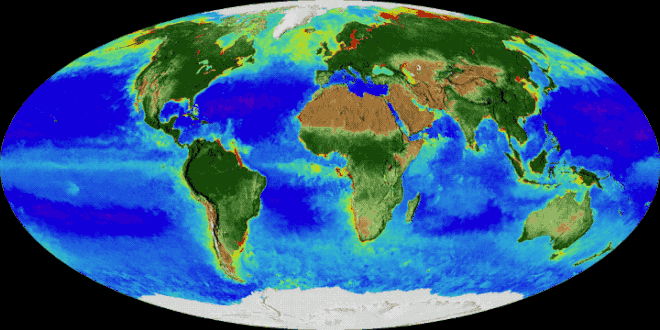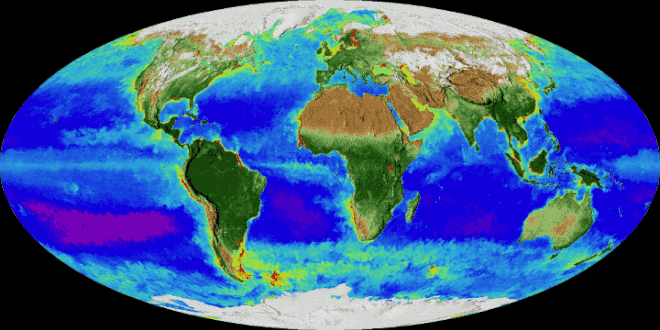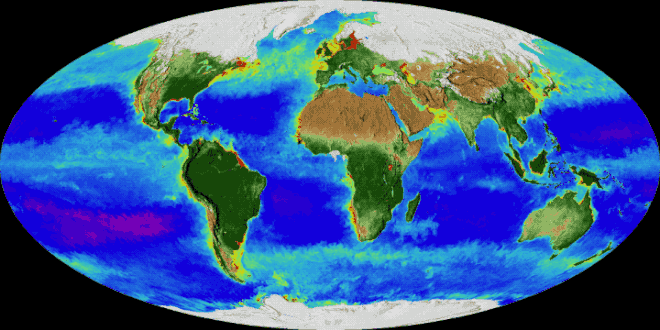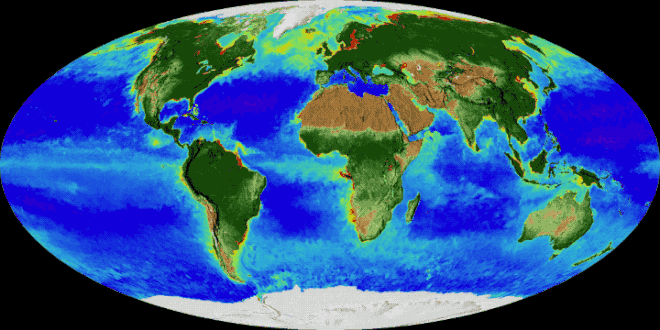 Image 9An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
Image 9An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
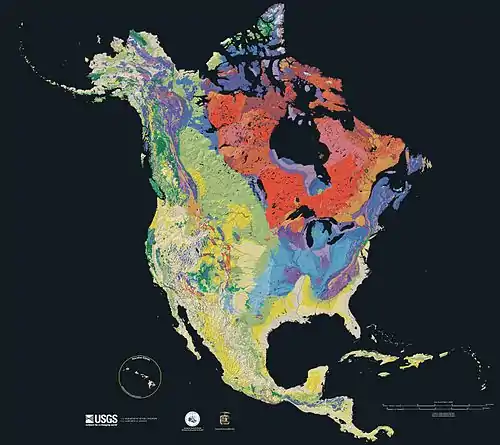 Image 11Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
Image 11Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.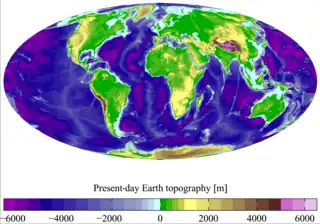
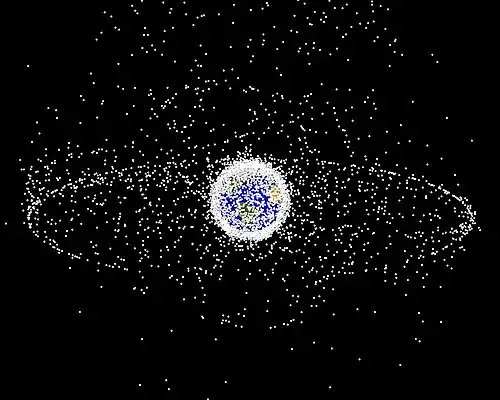 Image 13A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
Image 13A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth) Image 14Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
Image 14Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth) Image 15Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
Image 15Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)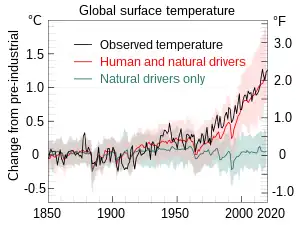 Image 16Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
Image 16Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth) Image 17Earth and the Moon as seen from Mars in an image taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on 22 April 2022 (from Earth)
Image 17Earth and the Moon as seen from Mars in an image taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on 22 April 2022 (from Earth)

 Image 20Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
Image 20Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth).jpg.webp) Image 21First airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
Image 21First airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
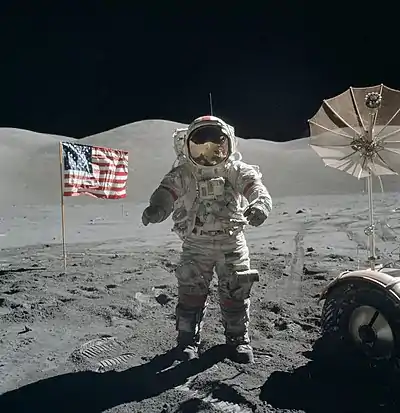 Image 23Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
Image 23Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
 Image 25A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
Image 25A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)

 Image 28A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
Image 28A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth) Image 29Battle during 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
Image 29Battle during 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan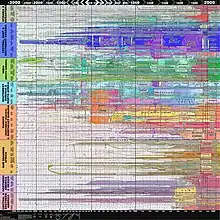 Image 30World history chart depicting state formation over time (from Human history)
Image 30World history chart depicting state formation over time (from Human history) Image 31"Lucy", the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found. Lucy was only 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) tall.
Image 31"Lucy", the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found. Lucy was only 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) tall.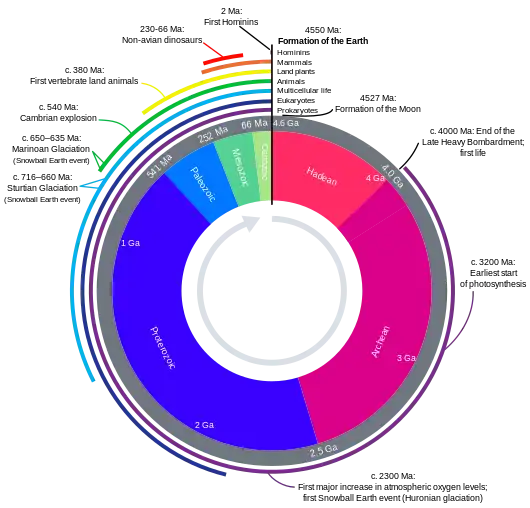

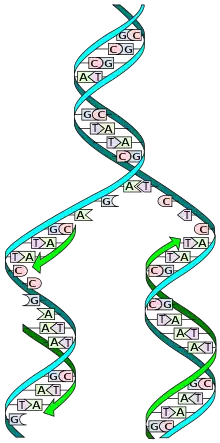 Image 34The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
Image 34The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
 Image 36A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
Image 36A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
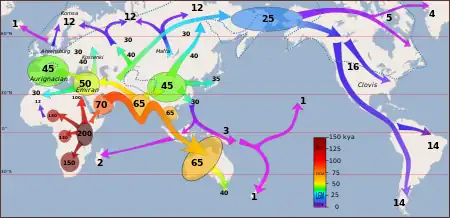 Image 38Map of peopling of the world (Southern Dispersal paradigm), in thousands of years ago.
Image 38Map of peopling of the world (Southern Dispersal paradigm), in thousands of years ago. Image 39Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
Image 39Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
 Image 41A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
Image 41A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)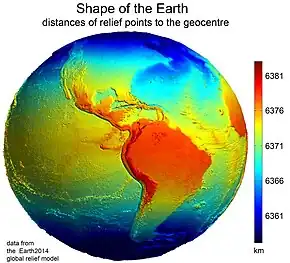 Image 42Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
Image 42Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth) Image 43A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
Image 43A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)

 Image 46An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as close than today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
Image 46An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as close than today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)

 Image 49Earth's atmosphere as it appears from space, as bands of different colours at the horizon. From the bottom, afterglow illuminates the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to just below the edge of space at one hundred kilometers and the pink line of airglow of the lower thermosphere (invisible), which hosts green and red aurorae over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
Image 49Earth's atmosphere as it appears from space, as bands of different colours at the horizon. From the bottom, afterglow illuminates the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to just below the edge of space at one hundred kilometers and the pink line of airglow of the lower thermosphere (invisible), which hosts green and red aurorae over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth) Image 50Empires of the world in 1898
Image 50Empires of the world in 1898
.svg.png.webp)
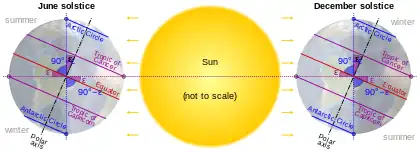 Image 53Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
Image 53Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth) Image 54A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
Image 54A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
 Image 56Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
Image 56Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
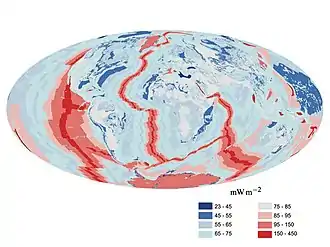 Image 58A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
Image 58A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth) Image 59Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
Image 59Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)


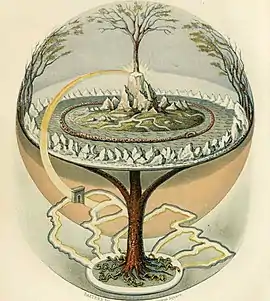 Image 64Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
Image 64Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World) Image 65Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
Image 65Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)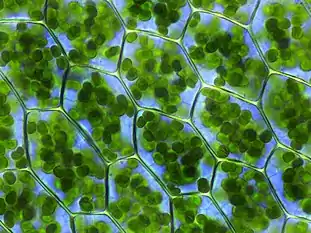 Image 66Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
Image 66Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth) Image 67Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
Image 67Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth) Image 68A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
Image 68A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
 Image 70Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
Image 70Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)

 Image 73Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
Image 73Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
 Image 75Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia, founded 670 CE
Image 75Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia, founded 670 CE Image 76Astronaut Buzz Aldrin on the Moon, photographed by Neil Armstrong, 1969 (from History of Earth)
Image 76Astronaut Buzz Aldrin on the Moon, photographed by Neil Armstrong, 1969 (from History of Earth) Image 77The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
Image 77The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)


 Image 81Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
Image 81Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)


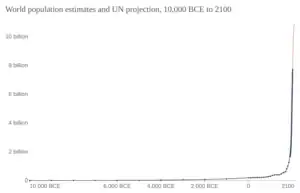 Image 85World population, from 10,000 BCE to 2000 CE, with projection to 2100 CE (from Human history)
Image 85World population, from 10,000 BCE to 2000 CE, with projection to 2100 CE (from Human history)
 Image 87An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
Image 87An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)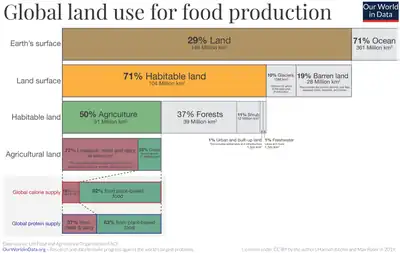 Image 88Earth's land use for human agriculture (from Earth)
Image 88Earth's land use for human agriculture (from Earth).jpeg.webp) Image 89Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
Image 89Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
 Image 91A pillar at Göbekli Tepe
Image 91A pillar at Göbekli Tepe
Megacities of the world -

Tokyo (/ˈtoʊkioʊ/; Japanese: 東京, Tōkyō, [toːkʲoː] ⓘ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis (東京都, Tōkyō-to), is the capital of Japan and the most populous city in the world with a population of over 14 million residents as of 2023. The Tokyo metropolitan area, which includes Tokyo and nearby prefectures, is the world's most-populous metropolitan area with 40.8 million residents .
Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, Tokyo is part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. (Full article...)Did you know -
- ... that deleted articles on Wikipedia may be "salted" so that they cannot be recreated?
- ... that during World War I, Roy W. Ritner was elected unopposed to the Oregon State Senate while serving with the American Red Cross in France?
- ... that Wrinkle Five Star set an unratified 1 km (0.62 mi) world record of 18 minutes 8 seconds while running in custom shoes?
- ... that Carol Wilson had to pretend that she was a schoolteacher when unofficially representing England at the 1971 Women's World Cup?
- ... that Lady Eva Julius once called Girl Guiding "the most important youth movement in the world"?
- ... that the archaeologist Alan Wace worked undercover for British intelligence during both world wars?
- ... that Taylor Swift said that her first live album, Speak Now World Tour – Live, was meant to capture what she wanted to "show [...] my kids and my grandkids"?
- ... that St Julian's Church was the only church in Norwich destroyed during World War II to be rebuilt?
Countries of the world -

Ivory Coast, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is the port city of Abidjan. It borders Guinea to the northwest, Liberia to the west, Mali to the northwest, Burkina Faso to the northeast, Ghana to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea (Atlantic Ocean) to the south. Its official language is French, and indigenous languages are also widely used, including Bété, Baoulé, Dioula, Dan, Anyin, and Cebaara Senufo. In total, there are around 78 different languages spoken in Ivory Coast. The country has a religiously diverse population, including numerous followers of Islam, Christianity, and traditional faiths like Animism.
Before its colonization, Ivory Coast was home to several states, including Gyaaman, the Kong Empire, and Baoulé. The area became a protectorate of France in 1843 and was consolidated as a French colony in 1893 amid the Scramble for Africa. It achieved independence in 1960, led by Félix Houphouët-Boigny, who ruled the country until 1993. Relatively stable by regional standards, Ivory Coast established close political-economic ties with its West African neighbours while maintaining close relations with the West, especially France. Its stability was diminished by a coup d'état in 1999 and two civil wars—first between 2002 and 2007 and again during 2010–2011. It adopted a new constitution in 2016. (Full article...)Related portals
Protected areas of the world -
 Image 1Protected areas of Eswatini include any geographical area protected for a specific use inside the landlocked country of Eswatini, in southern Africa.
Image 1Protected areas of Eswatini include any geographical area protected for a specific use inside the landlocked country of Eswatini, in southern Africa.
Within Eswatini there is a mix of national, private and community-owned protected areas. They include national parks, nature reserves, wildlife sanctuaries and game reserves. (Full article...) Image 2
Image 2 Grand Canyon of Yellowstone
Grand Canyon of Yellowstone
The protected areas of the United States are managed by an array of different federal, state, tribal and local level authorities and receive widely varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness, while others are operated with acceptable commercial exploitation. , the 42,826 protected areas covered 1,235,486 km2 (477,024 sq mi), or 13 percent of the land area of the United States. This is also one-tenth of the protected land area of the world. The U.S. also had a total of 871 National Marine Protected Areas, covering an additional 1,240,000 sq mi (3,200,000 km2), or 26 percent of the total marine area of the United States. (Full article...) Image 3Protected areas of Sri Lanka are administrated by Department of Forest Conservation and Department of Wildlife Conservation of Sri Lanka.There are 501 protected areas in Sri Lanka. The protected areas that fall under supervision of the Department of Forest Conservation include forests defined in National Heritage Wilderness Area Act in 1988, forest reservations, and forests managed for sustainability. Sinharaja Forest Reserve is an example for a National Heritage forest (it is also a World Heritage Site). There are 32 forests categorized as conservation forests including Knuckles Mountain Range. Strict nature reserves, national parks, nature reserves, forest corridors, and sanctuaries recognized under the Flora and Fauna Protection Ordinance are managed by Department of Wildlife Conservation. Total of all protected areas is 1,767,000 ha. Protected areas in Sri Lanka account for 26.5 percent of the total area. This is a higher percentage of protected areas than in all of Asia and much of the World. (Full article...)
Image 3Protected areas of Sri Lanka are administrated by Department of Forest Conservation and Department of Wildlife Conservation of Sri Lanka.There are 501 protected areas in Sri Lanka. The protected areas that fall under supervision of the Department of Forest Conservation include forests defined in National Heritage Wilderness Area Act in 1988, forest reservations, and forests managed for sustainability. Sinharaja Forest Reserve is an example for a National Heritage forest (it is also a World Heritage Site). There are 32 forests categorized as conservation forests including Knuckles Mountain Range. Strict nature reserves, national parks, nature reserves, forest corridors, and sanctuaries recognized under the Flora and Fauna Protection Ordinance are managed by Department of Wildlife Conservation. Total of all protected areas is 1,767,000 ha. Protected areas in Sri Lanka account for 26.5 percent of the total area. This is a higher percentage of protected areas than in all of Asia and much of the World. (Full article...) Image 4
Image 4 Rock carvings at the Ewaninga Rock Carvings Conservation Reserve
Rock carvings at the Ewaninga Rock Carvings Conservation Reserve
The protected areas of the Northern Territory consists of protected areas managed by the governments of the Northern Territory and Australia and private organisations with a reported total area of 335,527 square kilometres (129,548 sq mi) being 24.8% of the total area of the Northern Territory of Australia. (Full article...) Image 5Protected areas of the Caribbean are significant in a region of particular ecological vulnerability, including the impact of climate change and the impact of tourism.
Image 5Protected areas of the Caribbean are significant in a region of particular ecological vulnerability, including the impact of climate change and the impact of tourism.
The University of the West Indies' "Caribbean Protected Areas Gateway" supports informational resources for the 16 Caribbean member states of the Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States. It forms the regional component of the ACP's Biodiversity and Protected Areas Management program, building on the World Database on Protected Areas. (Full article...) Image 6Protected areas in the U.S. State of Ohio include national forest lands, Army Corps of Engineers areas, state parks, state forests, state nature preserves, state wildlife management areas, and other areas. (Full article...)
Image 6Protected areas in the U.S. State of Ohio include national forest lands, Army Corps of Engineers areas, state parks, state forests, state nature preserves, state wildlife management areas, and other areas. (Full article...)![Image 7Victoria is the smallest mainland state in Australia. As of 2022[update] it contained 5,081 separate protected areas with a total land area of 4,012,888 ha (9,916,060 acres) (17.64% of the state's area).The parks are managed by Parks Victoria, a state government agency. There are also many smaller state areas which are subject to commercial activity such as logging.class=notpageimage| National parks of Victoria State parks of Victoria Marine national parks of Victoria Marine and coastal parks of Victoria Marine sanctuaries of Victoria Other parks of Victoria (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 7Victoria is the smallest mainland state in Australia. As of 2022 it contained 5,081 separate protected areas with a total land area of 4,012,888 ha (9,916,060 acres) (17.64% of the state's area).
Image 7Victoria is the smallest mainland state in Australia. As of 2022 it contained 5,081 separate protected areas with a total land area of 4,012,888 ha (9,916,060 acres) (17.64% of the state's area).
The parks are managed by Parks Victoria, a state government agency. There are also many smaller state areas which are subject to commercial activity such as logging.(Full article...)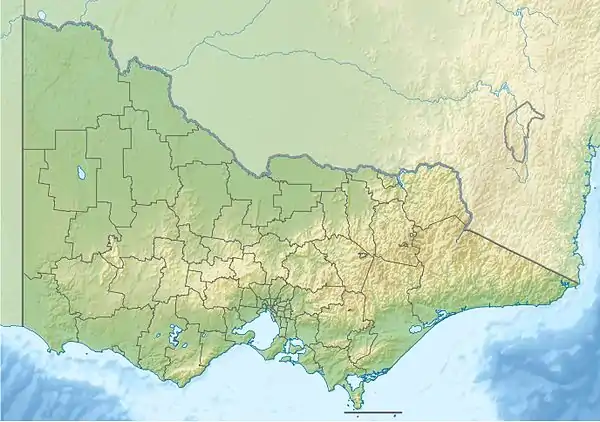












































































































 National parks of Victoria
National parks of Victoria  State parks of Victoria
State parks of Victoria  Marine national parks of Victoria
Marine national parks of Victoria  Marine and coastal parks of Victoria
Marine and coastal parks of Victoria  Marine sanctuaries of Victoria
Marine sanctuaries of Victoria  Other parks of Victoria
Other parks of Victoria Image 8
Image 8 Part of the Brecon Beacons National Park, looking from the highest point of Pen y Fan (886 m/2907 feet) to Cribyn (795 m/2608 feet).
Part of the Brecon Beacons National Park, looking from the highest point of Pen y Fan (886 m/2907 feet) to Cribyn (795 m/2608 feet).
Protected areas of the United Kingdom are areas in the United Kingdom which need and /or receive protection because of their environmental, historical or cultural value to the nation. Methods and aims of protection vary depending on the nature and importance of the resource. Protection operates at local, regional, national and international levels, and may be backed by legislation and international treaty, or less formally by planning policy.
Within the United Kingdom, different approaches are taken to some forms of protection within the constituent countries of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, while other forms of protection are more consistent across the UK. Protected areas can be divided according to the type of resource which each seeks to protect. Primarily, these are: scenic or landscape value; biodiversity value (species and habitats); geodiversity value (relating to geology and geomorphology); and cultural or historic value. Several types of protected areas are focused on more than one of these areas. (Full article...) Image 9
Image 9 The Valley of the Giants skywalk at Walpole-Nornalup National Park
The Valley of the Giants skywalk at Walpole-Nornalup National Park
Western Australia is the second largest country subdivision in the world.
As of 2022, based on the latest Collaborative Australian Protected Areas Database report, it contains 1857 separate land-based protected areas with a total area of 76,142,710 hectares (188,152,700 acres), accounting for just over 30 percent of the state's land mass. By area, Indigenous Protected Areas account for the largest part of this, almost 67 percent while, by number, nature reserves hold the majority with two-third of all land-based protected areas being nature reserves. (Full article...) Image 10
Image 10 Ludaš Lake is a shallow lake in the province of Vojvodina in northern Serbia, near the city of Subotica. It is a special natural preserve and, since 1977, designated as a swamp area of international significance by the Ramsar Convention.
Ludaš Lake is a shallow lake in the province of Vojvodina in northern Serbia, near the city of Subotica. It is a special natural preserve and, since 1977, designated as a swamp area of international significance by the Ramsar Convention.
Protected areas cover around 5% of the territory of Serbia. The Law on the Protection of the Nature defines these categories of protected areas:- Strict nature reserve — Area of unmodified natural features with representative ecosystems set aside for the preservation of its biodiversity and for scientific research and monitoring.
- Special nature reserve — Area of unmodified or slightly modified natural features of great importance due to uniqueness and rarity which includes the habitats of endangered species set aside for the preservation of its unique features, education, limited tourism and for scientific research and monitoring.
- National park — Area with large number of diverse ecosystems of national value, with outstanding natural features and/or cultural heritage set aside for the preservation of its natural resources and for educational, scientific and tourist use.
- Natural monument — Small unmodified or slightly modified natural feature, object or phenomenon, easily detectable and unique, with unique natural attributes.
- Protected habitat — Area which includes habitats of one or more wildlife species.
- Landscape of outstanding features — Area of remarkable appearance with important natural and cultural value.
- Nature park — Area of well-preserved natural values with preserved natural ecosystems and picturesque landscape set aside for the preservation of biodiversity and for educational, tourist, recreational and scientific use.
 Image 11A list of protected areas of Oman:
Image 11A list of protected areas of Oman:- Al Wusta Wildlife Reserve
- Ra's Al Hadd Turtle Reserve
- Ad Dimaniyat Islands Reserve
- Al Saleel National Park (As Salil Natural Park)
- Jabal Samhan Nature Reserve
- Al Jabal Al Akhdar Scenic Reserve
- Western Hajer Stars Lights Reserve
- Arabian Oryx Sanctuary
- Al Rustaq Wildlife Reserve
- Al Wusta Wetland Reserve
- Jabal Qahwan Nature Reserve
- Al Sareen Nature Reserve
- Ras al Shajar Nature Reserve
- Al Khuwuair Nature Reserve
- Khawrs of the Salalah Coast Reserve
- Khor Slalalah Nature Reserve
- Khawr al Mughsayl Reserve
- Khawr al Baleed Reserve
- Khawr Sawli Reserve
- Khawr al Dahareez Reserve
- Khawr Taqah Reserve
- Khawr Rawri Reserve
- Khawr Awqad Reserve
- Khawr al Qurum al Sagheer Reserve
- Khawr al Qurum al Kabeer Reserve
 Image 12The National Parks of Argentina make up a network of 35 national parks in Argentina. The parks cover a very varied set of terrains and biotopes, from Baritú National Park on the northern border with Bolivia to Tierra del Fuego National Park in the far south of the continent. The Administración de Parques Nacionales (National Parks Administration) is the agency that preserves and manages these national parks along with Natural monuments and National Reserves within the country.
Image 12The National Parks of Argentina make up a network of 35 national parks in Argentina. The parks cover a very varied set of terrains and biotopes, from Baritú National Park on the northern border with Bolivia to Tierra del Fuego National Park in the far south of the continent. The Administración de Parques Nacionales (National Parks Administration) is the agency that preserves and manages these national parks along with Natural monuments and National Reserves within the country.
The headquarters of the National Parks Service are in downtown Buenos Aires, on Santa Fe Avenue. A library and information centre are open to the public. The administration also covers the national monuments, such as the Jaramillo Petrified Forest, and natural and educational reserves. (Full article...) Image 13Protected areas of Canada consist of approximately 12.1 percent of the nation's landmass and freshwater are considered conservation areas, including 11.4 percent designated as protected areas. Approximately 13.8 percent of Canada's territorial waters are conserved, including 8.9 percent designated as protected areas. Terrestrial areas conserved have increased by 65 percent in the 21st century, while marine areas conserved have increased by more than 3,800 percent.
Image 13Protected areas of Canada consist of approximately 12.1 percent of the nation's landmass and freshwater are considered conservation areas, including 11.4 percent designated as protected areas. Approximately 13.8 percent of Canada's territorial waters are conserved, including 8.9 percent designated as protected areas. Terrestrial areas conserved have increased by 65 percent in the 21st century, while marine areas conserved have increased by more than 3,800 percent.
Conservation and protected areas have different mandates depending on the organization which manages them, with some areas having a greater focus on ecological integrity, historical preservation, public usage, scientific research, or a combination of usages. Some areas such as the Polar Bear Pass, are co-managed and overseen by government and local indigenous agencies. (Full article...) Image 14The state of Johor in Malaysia is noted for its national parks and forest reserves which preserve virgin rainforests known for its biodiversity and endangered species of animals.
Image 14The state of Johor in Malaysia is noted for its national parks and forest reserves which preserve virgin rainforests known for its biodiversity and endangered species of animals.
Mangrove swamps and coral reefs are also protected within these parks. (Full article...) Image 15
Image 15 Vegetation outside Goz Beïda
Vegetation outside Goz Beïda
The wildlife of Chad is composed of its flora and fauna. Bush elephants, West African lions, buffalo, hippopotamuses, Kordofan giraffes, antelopes, African leopards, cheetahs, hyenas, and many species of snakes are found there, although most large carnivore populations have been drastically reduced since the early 20th century. Elephant poaching, particularly in the south of the country in areas such as Zakouma National Park, is a severe problem. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
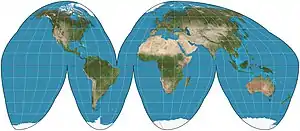 Image 1The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
Image 1The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.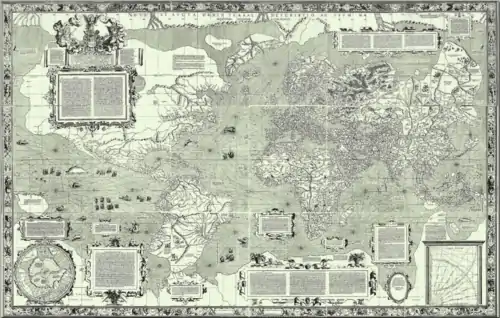 Image 2The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
Image 2The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection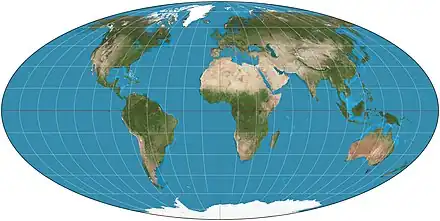 Image 3Mollweide projection of the world
Image 3Mollweide projection of the world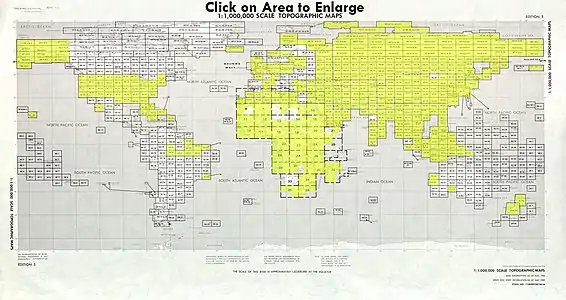 Image 4Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
Image 4Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)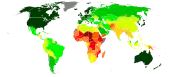 Image 5United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
Image 5United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)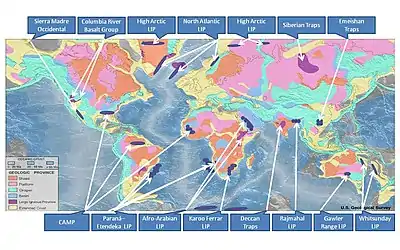 Image 6Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
Image 6Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data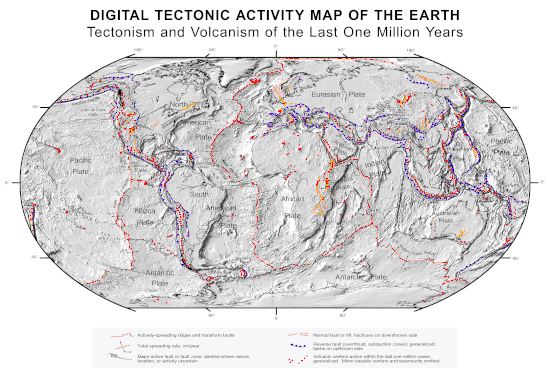 Image 7A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
Image 7A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles Image 81516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
Image 81516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller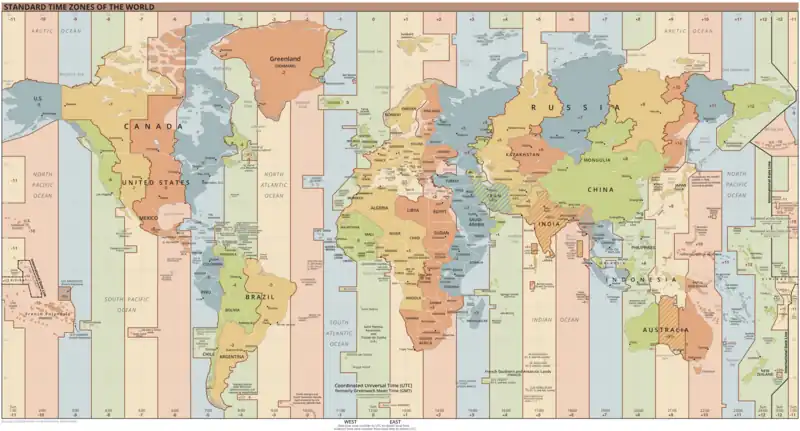 Image 9Time zones of the world
Image 9Time zones of the world
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousands years ago); Ma = megaannum (millions years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billions years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards |
|
| Summer Games |
| |
|---|---|---|
| Winter Games |
| |
| ||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
_political.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
