 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
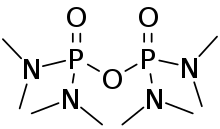
| Preferred IUPAC name
Octamethyldiphosphoric tetraamide | |
| Other names
OMPA, Octamethyl pyrophosphoramide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.275 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3018 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H24N4O3P2 | |
| Molar mass | 286.253 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.09 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H300, H310, H330, H371, H373, H412 | |
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P350, P304+P340, P309+P311, P310, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Schradan, named after Gerhard Schrader, is an obsolete organophosphate insecticide.[1] Schradan itself is a weak cholinesterase inhibitor and requires metabolic activation to become active.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ GARDINER, JE; KILBY, BA (April 1952). "Biochemistry of organic phosphorus insecticides. I. The mammalian metabolism of bis(dimethylamino) phosphonous anhydride (Schradan)". The Biochemical Journal. 51 (1): 78–85. doi:10.1042/bj0510078. PMC 1197790. PMID 14944535.
- ↑ DAVISON, AN (October 1955). "The conversion of schra dan (OMPA) and parathion into inhibitors of cholinesterase by mammalian liver". The Biochemical Journal. 61 (2): 203–9. doi:10.1042/bj0610203. PMC 1215773. PMID 13260199.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.