The systems science portal
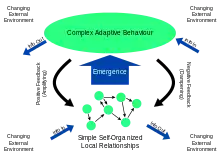 |
| Complex systems approach |
Systems science is an transdisciplinary[1] field that studies the nature of systems—from simple to complex—in nature, society, cognition, engineering, technology and science itself. To systems scientists, the world can be understood as a system of systems. The field aims to develop interdisciplinary foundations that are applicable in a variety of areas, such as psychology, biology, medicine, communication, business management, engineering, and social sciences.
Systems science covers formal sciences such as complex systems, cybernetics, dynamical systems theory, information theory, linguistics or systems theory. It has applications in the field of the natural and social sciences and engineering, such as control theory, operations research, social systems theory, systems biology, system dynamics, human factors, systems ecology, systems engineering and systems psychology. Themes commonly stressed in system science are (a) holistic view, (b) interaction between a system and its embedding environment, and (c) complex (often subtle) trajectories of dynamic behavior that sometimes are stable (and thus reinforcing), while at various 'boundary conditions' can become wildly unstable (and thus destructive). Concerns about Earth-scale biosphere/geosphere dynamics is an example of the nature of problems to which systems science seeks to contribute meaningful insights.
Selected article -
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes, and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community.
An economic system is a type of social system. The mode of production is a related concept. All economic systems must confront and solve the four fundamental economic problems:
- What kinds and quantities of goods shall be produced: This fundamental economic problem is anchored on the theory of pricing. The theory of pricing, in this context, has to do with the economic decision-making between the production of capital goods and consumer goods in the economy in the face of scarce resources. In this regard, the critical evaluation of the needs of the society based on population distribution in terms of age, sex, occupation, and geography is very pertinent.
- How goods shall be produced: The fundamental problem of how goods shall be produced is largely hinged on the least-cost method of production to be adopted as gainfully peculiar to the economically decided goods and services to be produced. On a broad note, the possible production method includes labor-intensive and capital-intensive methods.
- How the output will be distributed: Production is said to be completed when the goods get to the final consumers. This fundamental problem of how the output will be distributed seeks to identify the best possible medium through which bottlenecks and the clogs in the wheel of the chain of economic resources distributions can reduce to the barest minimum and optimize consumers' satisfaction.
- When to produce: Consumer satisfaction is partly a function of seasonal analysis as the forces of demand and supply have a lot to do with time. This fundamental economic problem requires an intensive study of time dynamics and seasonal variation vis-a-vis the satisfaction of consumers' needs. It is noteworthy to state that solutions to these fundamental problems can be determined by the type of economic system. (Full article...)
Selected picture

An aerial view of a human ecosystem. Pictured is the city of Chicago.
'WikiProjects
- Wikiproject Systems
- WikiProject Science
- WikiProject Philosophy
- WikiProject History of Science
Selected biography -
Edward René David Goldsmith (8 November 1928 – 21 August 2009), widely known as Teddy Goldsmith, was an Anglo-French environmentalist, writer and philosopher.
He was a member the prominent Goldsmith family. The eldest son of Major Frank Goldsmith, and elder brother of the financier James Goldsmith. Edward Goldsmith was the founding editor and publisher of The Ecologist. Known for his outspoken views opposing industrial society and economic development, he expressed a strong sympathy for the ways and values of traditional peoples. (Full article...)Did you know
- ... that the American neurophysiologist Ralph W. Gerard late 1940s developed an intracellular recording microelectrode, that revolutionized research in neurobiology?
- ... * continuing vertically with a science of design,
- ... that the anthropologist, linguist, and cyberneticist Gregory Bateson's most noted writings are Steps to an Ecology of Mind (1972) and Mind and Nature (1980).
- ... that a multi-agent system (MAS) is a system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents, which can be used to solve problems which are impossible for monolithic system to solve.
Categories
Related portals
Topics
Tasks
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Associated Wikimedia
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals