The Nicaragua Portal
Nicaragua (/ˌnɪkəˈrɑːɡwə, -ˈræɡ-, -ɡjuə/ ⓘ; Spanish: [nikaˈɾaɣwa] ⓘ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (ES-pe - República de Nicaragua.ogg), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. it was estimated to be the third largest city in Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, Indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English. Originally inhabited by various indigenous cultures since ancient times, the region was conquered by the Spanish Empire in the 16th century. Nicaragua gained independence from Spain in 1821. The Mosquito Coast followed a different historical path, being colonized by the English in the 17th century and later coming under British rule. It became an autonomous territory of Nicaragua in 1860 and its northernmost part was transferred to Honduras in 1960. Since its independence, Nicaragua has undergone periods of political unrest, dictatorship, occupation and fiscal crisis, including the Nicaraguan Revolution of the 1960s and 1970s and the Contra War of the 1980s. (Full article...) Selected article -José Daniel Ortega Saavedra (Spanish pronunciation: [daˈnjel oɾˈteɣa]; born 11 November 1945) is a Nicaraguan politician who has served as President of Nicaragua since 2007. Previously he was leader of Nicaragua from 1979 to 1990, first as coordinator (1979–1985) of the Junta of National Reconstruction, and then as President of Nicaragua (1985–1990). During his first term, he implemented policies to achieve leftist reforms across Nicaragua. In later years, Ortega's left-wing radical politics cooled significantly, leading him to pursue pro-business policies and even rapprochement with the Catholic Church. As a part of this, his government adopted strong anti-abortion policies, and his rhetoric took on a new, strongly religious tenor, despite formerly having professed atheism. Ortega came to prominence with the overthrow and exile of US-backed dictator Anastasio Somoza Debayle in 1979 during the Nicaraguan Revolution. As a leader in the Sandinista National Liberation Front (Spanish: Frente Sandinista de Liberación Nacional, FSLN) Ortega became leader of the ruling Junta of National Reconstruction. A Marxist–Leninist, Ortega pursued a program of nationalization, land reform, wealth redistribution and literacy programs during his first period in office. Ortega's government was responsible for the forced displacement of 10,000 indigenous people. In 1984, Ortega won Nicaragua's first ever free and fair presidential election with over 60% of the vote as the FSLN's candidate. Throughout the 1980s, Ortega's government faced a rebellion by US-backed rebels, known as the Contras. The US also sought to place economic pressure on the Sandinista government, imposing a full trade embargo, and planting underwater mines in Nicaragua's ports. After a presidency marred by conflict and economic collapse, Ortega was defeated in the 1990 Nicaraguan general election by Violeta Chamorro, in an election marked by US interference. (Full article...)Did you know...
Related portalsWikiProjectsWikiProject Central America
Selected image -SubcategoriesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Nicaragua Nicaragua-related lists Buildings and structures in Nicaragua Nicaraguan culture Economy of Nicaragua Education in Nicaragua Environment of Nicaragua Geography of Nicaragua Government of Nicaragua Health in Nicaragua History of Nicaragua Organizations based in Nicaragua Nicaraguan people Politics of Nicaragua Society of Nicaragua Nicaragua stubs Nicaragua newsThings you can do
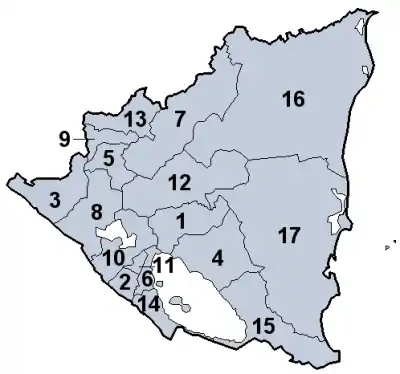
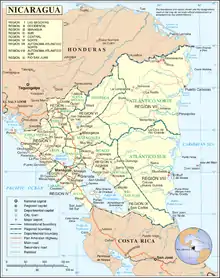
Nicaragua TopicsDepartmentsNicaragua is a unitary republic. For administrative purposes it is divided into 15 departments (departamentos) and two self-governing regions (autonomous regions). (Department capitals in parentheses) Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Sources
Discover Wikipedia using portals
| ||||||||||


%E9%9B%99%E9%82%8A%E6%9C%83%E6%99%A4_(32074399712)_(cropped).jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)
_in_Nicaragua.jpg.webp)