Welcome to the Israel Portal |
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject Israel}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
Featured articles
 1940 Mandatory Palestine v Lebanon football match
1940 Mandatory Palestine v Lebanon football match Acra (fortress)
Acra (fortress) Afroyim v. Rusk
Afroyim v. Rusk Princess Alice of Battenberg
Princess Alice of Battenberg Balfour Declaration
Balfour Declaration Joel Brand
Joel Brand Killing of Muhammad al-Durrah
Killing of Muhammad al-Durrah International Conference on the Holocaust and Genocide
International Conference on the Holocaust and Genocide Otto Klemperer
Otto Klemperer Levantine Arabic
Levantine Arabic Second Crusade
Second Crusade Richard Williams (RAAF officer)
Richard Williams (RAAF officer)
Featured lists
A-Class articles
Good articles
 6th Airborne Division in Palestine
6th Airborne Division in Palestine 69 Squadron (Israel)
69 Squadron (Israel) 1958 FIFA World Cup qualification (AFC/CAF–UEFA play-off)
1958 FIFA World Cup qualification (AFC/CAF–UEFA play-off) 1982 kidnapping of Iranian diplomats
1982 kidnapping of Iranian diplomats Abergil Organization
Abergil Organization AIL Storm
AIL Storm American Palestine Line
American Palestine Line Angel Bakeries
Angel Bakeries Al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque Arab Christians
Arab Christians Armenian Quarter
Armenian Quarter Arrow (missile family)
Arrow (missile family) Assassination of Iranian nuclear scientists
Assassination of Iranian nuclear scientists Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz concentration camp Deni Avdija
Deni Avdija Ayyubid dynasty
Ayyubid dynasty BYU Jerusalem Center
BYU Jerusalem Center Ralph Bakshi
Ralph Bakshi Franzisca Baruch
Franzisca Baruch Battle of Fort Lahtzanit
Battle of Fort Lahtzanit Battle of Karameh
Battle of Karameh Battle of the Chinese Farm
Battle of the Chinese Farm Battle of Jerusalem
Battle of Jerusalem Battle of Tawahin
Battle of Tawahin Battles of the Kinarot Valley
Battles of the Kinarot Valley Bayt Jibrin
Bayt Jibrin Bethlehem
Bethlehem Biblical Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew Birket Israel
Birket Israel Al-Birwa
Al-Birwa Black Hebrew Israelites
Black Hebrew Israelites Murder of Dora Bloch
Murder of Dora Bloch Amir Blumenfeld
Amir Blumenfeld Clal Center
Clal Center Comverse Technology
Comverse Technology Crusades
Crusades Cyrus Cylinder
Cyrus Cylinder Adolf Eichmann
Adolf Eichmann Eilat Airport
Eilat Airport Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein EL/M-2080 Green Pine
EL/M-2080 Green Pine Eurovision Song Contest 1999
Eurovision Song Contest 1999 Falafel
Falafel Fill the Void
Fill the Void First Crusade
First Crusade Battles of Fort Budapest
Battles of Fort Budapest Zvi Hecker
Zvi Hecker Historiography of the Crusades
Historiography of the Crusades History of the Jews in Mauritius
History of the Jews in Mauritius The Holocaust
The Holocaust Hurva Synagogue
Hurva Synagogue Ir Ovot
Ir Ovot Battle of Ismailia
Battle of Ismailia Israel at the 2010 Winter Olympics
Israel at the 2010 Winter Olympics Israel at the 2016 Summer Olympics
Israel at the 2016 Summer Olympics Israeli citizenship law
Israeli citizenship law Downtown Triangle (Jerusalem)
Downtown Triangle (Jerusalem) 2008 Jerusalem bulldozer attack
2008 Jerusalem bulldozer attack Jews in Hong Kong
Jews in Hong Kong John of Brienne
John of Brienne Joseph's Tomb
Joseph's Tomb Kashrut
Kashrut Ian Kinsler
Ian Kinsler Kvitel
Kvitel Battles of Latrun (1948)
Battles of Latrun (1948) Ryan Lavarnway
Ryan Lavarnway Micah Joseph Lebensohn
Micah Joseph Lebensohn Lemon Tree (2008 film)
Lemon Tree (2008 film) David Levin (ice hockey)
David Levin (ice hockey) Liviu Librescu
Liviu Librescu Mamilla Mall
Mamilla Mall Mamilla
Mamilla McMahon–Hussein Correspondence
McMahon–Hussein Correspondence Mishmar HaEmek
Mishmar HaEmek Operation Mole Cricket 19
Operation Mole Cricket 19 Mosaic of Rehob
Mosaic of Rehob Nabataean Aramaic
Nabataean Aramaic Nakam
Nakam Nazis and Nazi Collaborators (Punishment) Law
Nazis and Nazi Collaborators (Punishment) Law Never again
Never again One Million Plan
One Million Plan Operation Pleshet
Operation Pleshet Origen
Origen Neri Oxman
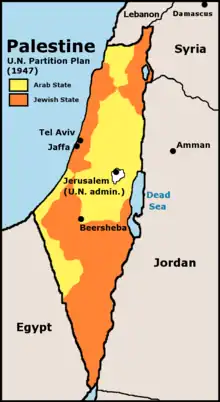
Neri Oxman Mandate for Palestine
Mandate for Palestine Palestine (region)
Palestine (region) Palestinian enclaves
Palestinian enclaves Paper Brigade
Paper Brigade Peasants' revolt in Palestine
Peasants' revolt in Palestine Natalie Portman
Natalie Portman Joshua Prawer
Joshua Prawer Qualifying industrial zone
Qualifying industrial zone Robinson's Arch
Robinson's Arch Roman Empire
Roman Empire Royal Stoa (Jerusalem)
Royal Stoa (Jerusalem) Russian language in Israel
Russian language in Israel Battle of Samakh
Battle of Samakh Samson
Samson Oskar Schindler
Oskar Schindler Anton Schmid
Anton Schmid Schneller Orphanage
Schneller Orphanage Sde Dov Airport
Sde Dov Airport Schwester Selma
Schwester Selma Ida Silverman
Ida Silverman Hillel Slovak
Hillel Slovak Bassem Tamimi
Bassem Tamimi Chaim Topol
Chaim Topol Danny Valencia
Danny Valencia Warsaw concentration camp
Warsaw concentration camp Western Wall
Western Wall Simon Wiesenthal
Simon Wiesenthal Yad Kennedy
Yad Kennedy Zion Square
Zion Square
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
External media
Mass media in Israel (in English):
Sources
- ↑ Butcher, Tim. Sharon presses for fence across Sinai, Daily Telegraph, December 07, 2005.
- ↑ cite web| title=11 Jan, 2010; from google (Israel–Egypt barrier construction began) result 8|url=https://www.rt.com/politics/israel-approves-democratic-barrier/}}
- ↑ "November 22, 2010; from google (Israel–Egypt barrier construction began) result 10".
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals





.jpg.webp)





.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)


-Aerial-Temple_Mount-(south_exposure).jpg.webp)


















._Visual_History_of_Nations%252C_Israel_(1948)%252C_New_Canaan%252C_CT.jpg.webp)
.PNG.webp)
_-_Gold_Medalist_Windsurfer_Gal_Fridman_(1).jpg.webp)
















_-_Defense_Minister_Moshe_Dayan%252C_Chief_of_staff_Yitzhak_Rabin%252C_Gen._Rehavam_Zeevi_(R)_And_Gen._Narkis_in_the_old_city_of_Jerusalem.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)


_-_Patriot_missiles_being_launched_to_intercept_an_Iraqi_Scud_missile.jpg.webp)











_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)
