IntroductionCommunism (from Latin communis, 'common, universal') is a left-wing to far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered around common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange that allocates products to everyone in the society based on need. A communist society would entail the absence of private property and social classes, and ultimately money and the state (or nation state). Communists often seek a voluntary state of self-governance but disagree on the means to this end. This reflects a distinction between a more libertarian socialist approach of communization, revolutionary spontaneity, and workers' self-management, and a more authoritarian vanguardist or communist party-driven approach through the development of a socialist state, followed by the withering away of the state. As one of the main ideologies on the political spectrum, communism is placed on the left-wing alongside socialism, and communist parties and movements have been described as radical left or far-left. Variants of communism have been developed throughout history, including anarchist communism, Marxist schools of thought, and religious communism, among others. Communism encompasses a variety of schools of thought, which broadly include Marxism, Leninism, and libertarian communism, as well as the political ideologies grouped around those. All of these different ideologies generally share the analysis that the current order of society stems from capitalism, its economic system, and mode of production, that in this system there are two major social classes, that the relationship between these two classes is exploitative, and that this situation can only ultimately be resolved through a social revolution. The two classes are the proletariat, who make up the majority of the population within society and must sell their labor power to survive, and the bourgeoisie, a small minority that derives profit from employing the working class through private ownership of the means of production. According to this analysis, a communist revolution would put the working class in power, and in turn establish common ownership of property, the primary element in the transformation of society towards a communist mode of production. Communism in its modern form grew out of the socialist movement in 19th-century Europe, which blamed capitalism for the misery of urban factory workers. In the 20th century, several ostensibly Communist governments espousing Marxism–Leninism and its variants came into power, first in the Soviet Union with the Russian Revolution of 1917, and then in portions of Eastern Europe, Asia, and a few other regions after World War II. As one of the many types of socialism, communism became the dominant political tendency, along with social democracy, within the international socialist movement by the early 1920s. (Full article...) Selected article
The Shining Path is classified by the Peruvian government, the U.S., the European Union, and Canada as a terrorist organization. Since the capture of its leader Abimael Guzmán in 1992, the Shining Path has declined in activity. Selected biography.jpg.webp)
Kádár was born in Fiume to a poor family, his father left his mother and him when he was very young, and he never met his father. After living in the countryside for some years, Kádár and his mother moved to Budapest. After quitting school, Kádár joined the Communist Party of Hungary's youth organisation, KIMSZ. Kádár would go on to become a prominent figure in the pre-World War II communist party, even becoming First Secretary. As leader he dissolved the party, and reorganised it as the Peace Party. This new party failed to win any popular support for the communist cause, and he would later be accused, of dissolving the Hungarian communist party. With the German invasion of Hungary, the Peace Party tried again to win support from the Hungarian populace, but failed. At the time of the Soviet occupation, the communists led by Kádár were very small in size. As leader of Hungary, Kádár was a team player, and took care to consult his colleagues before acting or making decisions, and his tenure saw an attempt at liberalising the economic system to put greater effort to build up industries aimed at consumers. His rule was marked by what later became known as 'Goulash Communism'. A significant increase in consumer expenditures because of the New Economic Mechanism (NEM), a major economic reform, reintroduced certain market mechanisms into Hungary. As a result of the relatively high standard of living, and more relaxed travel restrictions than those present in other Eastern Bloc countries, Hungary was generally considered the best country to live in Central and Eastern Europe during the Cold War, also expressed in the informal term "the happiest barrack". On 6 July 1989, an ill Kádár died, after having been forced to retire. Did you know...
Selected image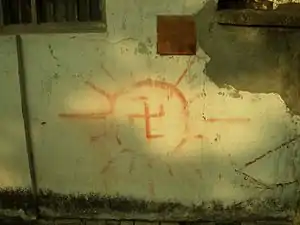 Election mural of the Communist Party of Nepal (Unified Marxist-Leninist). In Nepal the swastika is used as a voting symbol in ballots.
Photo credit: Soman News related to communism
Related portalsRelated Wikiprojects
Related featured content Featured Articles: Participate!Everyone is welcome to participate in WikiProject Socialism, where editors collaborate to improve all aspects related to socialism on Wikipedia. Selected quote"The lower middle class, the small manufacturer, the shopkeeper, the artisan, the peasant, all these fight against the bourgeoisie, to save from extinction their existence as fractions of the middle class. They are therefore not revolutionary, but conservative. Nay more, they are reactionary, for they try to roll back the wheel of history. If by chance, they are revolutionary, they are only so in view of their impending transfer into the proletariat; they thus defend not their present, but their future interests, they desert their own standpoint to place themselves at that of the proletariat. The “dangerous class”, (lumpenproletariat) the social scum, that passively rotting mass thrown off by the lowest layers of the old society, may, here and there, be swept into the movement by a proletarian revolution; its conditions of life, however, prepare it far more for the part of a bribed tool of reactionary intrigue."
SubcategoriesWant to find an article related to communism? Try browsing through any of the main categories below:
Category puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Communism Communism in the Arab world Communism in the Middle East Communists Communism by continent Communism by country Communism templates Communist states Anarcho-communism Anti-communism Christian communism Communism-based civil wars Criticism of communism Early Soviet republics Former communist economies Former socialist republics Hammer and sickle Historians of communism Imperialism studies Jewish communist movements Juche Leninism Marxian economics Marxism Marxism–Leninism Mass killings by communist regimes National communism Neo-Babouvism Communist nostalgia Communist organizations Paris Commune Communist press festivals Communist propaganda Communist rebellions Communist repression Soviet republics Television episodes about communism Communist terminology Communist terrorism Communist theory Communist works Works about communism Writers about communism Communism-related topics
GeneralVariations of CommunismOrganizations and ruling parties, past and present
Personalities
Present and former Socialist states (under the direction of Communist parties)
Ideology and tactics
StructureMarxian economics topicsHistorical events
Military topics
Artists and writers
Influential works
Anti-communism
Communism-related listsThings you can do
Communism in non-English WikipediasArticles:
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|
