| Main page | Categories & Main topics | Tasks and Projects |
The Aviation Portal
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. Aircraft includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships.
Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. (Full article...)
Selected article
The word 'helicopter' is adapted from the French hélicoptère, coined by Gustave de Ponton d'Amecourt in 1861, which originates from the Greek helix/helik- (ἕλικ-) = 'spiral' or 'turning' and pteron (πτερόν) = 'wing'.
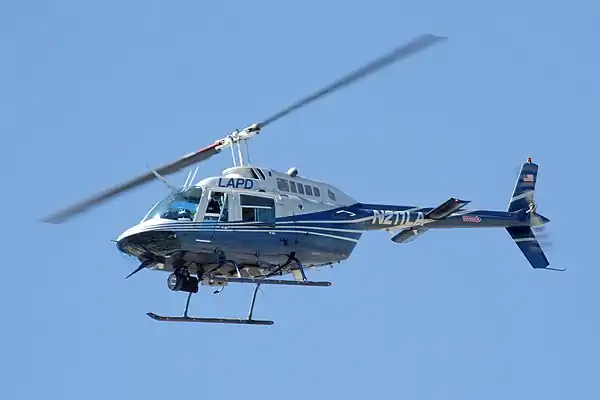
Helicopters were developed and built during the first half-century of flight, with some reaching limited production, but it was not until 1942 that a helicopter designed by Igor Sikorsky reached full-scale production, with 131 aircraft built. Though most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, it was the single main rotor with antitorque tail rotor configuration of this design that would come to be recognized worldwide as the helicopter. (Full article...)
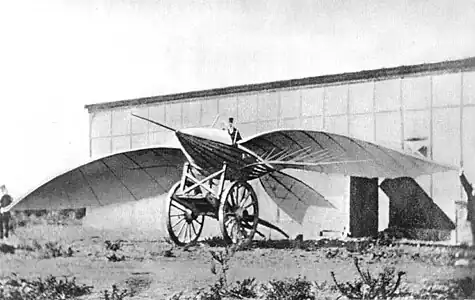
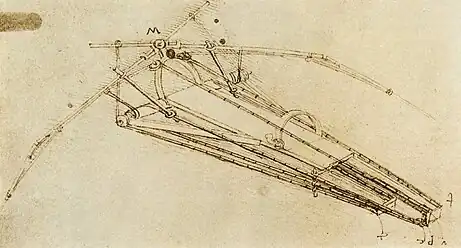
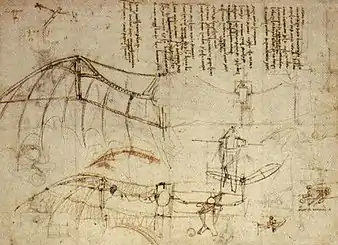
Selected image

Did you know
...that after the Red Baron, French ace René Fonck had the most confirmed World War I aerial victories? ... that the Air Zoo in Kalamazoo, Michigan houses the only SR-71B Blackbird in existence? ...that the strategic bombing campaign used in the 1990 Operation Instant Thunder served as a model for subsequent American military conflicts?
General images -
In the news
- May 29: Austrian Airlines cancels Moscow-bound flight after Russia refuses a reroute outside Belarusian airspace
- August 8: Passenger flight crashes upon landing at Calicut airport in India
- June 4: Power firm helicopter strikes cables, crashes near Fairfield, California
- January 29: Former basketball player Kobe Bryant dies in helicopter crash, aged 41
- January 13: Iran admits downing Ukrainian jet, cites 'human error'
- January 10: Fire erupts in parking structure at Sola Airport, Norway
- October 27: US announces restrictions on flying to Cuba
- October 3: World War II era plane crashes in Connecticut, US, killing at least seven
- September 10: Nevada prop plane crash near Las Vegas leaves two dead, three injured
- August 6: French inventor Franky Zapata successfully crosses English Channel on jet-powered hoverboard
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Selected biography
Amy Johnson (1 July 1903 – 5 January 1941) C.B.E. was a pioneering British aviatrix.
Born in Kingston upon Hull, Johnson graduated from University of Sheffield with a Bachelor of Arts in economics. She was introduced to flying as a hobby, gaining a pilot's A Licence No. 1979 on 6 July 1929 at the London Aeroplane Club. In that same year, she became the first British woman to gain a ground engineer's C License.
Johnson achieved worldwide recognition when, in 1930, she became the first woman to fly solo from England to Australia. She left Croydon on 5 May of that year and landed in Darwin, Australia on 24 May after flying 11,000 miles. Her aircraft for this flight, a De Havilland Gipsy Moth (registration G-AAAH) named Jason, can still be seen in the Science Museum in London. She received the Harmon Trophy as well as a CBE in homage to this achievement, and was also honoured with the No. 1 civil pilot's licence under Australia's 1921 Air Navigation Regulations.
In July 1931, Johnson and her co-pilot Jack Humphreys became the first pilots to fly from London to Moscow in one day, completing the 1,760-mile journey in approximately 21 hours. From there, they continued across Siberia and on to Tokyo, setting a record time for flying from England to Japan. The flight was completed in a De Havilland Puss Moth.
Selected Aircraft

The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is an American four-engine heavy bomber aircraft developed for the U.S. Army Air Corps (USAAC). Competing against Douglas and Martin for a contract to build 200 planes, the airplane outperformed both the other entries and the Air Corps' expectations. Although losing the contract due to an accident, the Air Corps was so in favor of the B-17 that they ordered 13 B-17s regardless. Evolving through numerous design stages, from B-17A to G, the Flying Fortress is considered the first truly mass-produced large aircraft. From its pre-war inception, the USAAC touted the aircraft as a strategic weapon; it was a high-flying, long-ranging potent bomber capable of defending itself. With the ability to return home despite extensive battle damage, its durability, especially in belly-landings and ditchings, quickly took on mythical proportions.
The B-17 was primarily involved in the daylight precision strategic bombing campaign of World War II against German industrial targets. The United States Eighth Air Force based in England and the Fifteenth Air Force based in Italy complemented the RAF Bomber Command's night-time area bombing in Operation Pointblank, which helped secure air superiority over the cities, factories and battlefields of Western Europe in preparation for Operation Overlord. The B-17 also participated, to a lesser extent, in the War in the Pacific.
Today in Aviation
- 2012 – 2012 Aéro-Service Ilyushin Il-76T crash: An Aéro-Service (initially mistakenly attributed to Trans Air Congo[1]) Ilyushin Il-76T (registration number EK-76300) on a domestic cargo flight in the Republic of the Congo from Pointe Noire to Brazzaville crashes short of Runway 5L in a residential area while attempting to land in bad weather at Maya-Maya Airport in Brazzaville.[2] All six crew members – five of whom are from Armenia – and one police officer on board the aircraft and 26 people on the ground are killed, and 14 people on the ground are injured.[1]
- 2009 – An Indian Air Force Sukhoi Su-30MKI crashes near Jethagaon in Jaisalmer of Rajasthan after it took off from Jodhpur, crash happened while returning from a regular training mission, both pilots are safe.
- 2000 – Launch: Space Shuttle Endeavour STS-97 at 22:06 EST. Mission highlights: ISS assembly flight 4A: P6 solar arrays, radiators.
- 2007 – Atlasjet Flight 4203, an MD-83 registered TC-AKM, crashed shortly after departure out of Atatürk International Airport in Istanbul, Turkey, killing all 57 on board. With good weather and no known technical issues, it was determined that the crash was caused due to the pilot experiencing spatial disorientation.
- 2004 – Lion Air Flight 538, a McDonnell Douglas MD-82, crash-lands in Solo City, Indonesia, killing 25 of the 154 people on board.
- 2000 – Marc Garneau made his third and final space flight aboard Endeavour on STS-97.
- 1999 – British Aerospace and Marconi Electronic Systems merged to form BAE Systems, Europe’s largest defense contractor and the fourth largest aerospace firm in the world.
- 1991 – During routine training mission, pilot Lt. Michael Young, 28, bailed out of his disabled USAF LTV A-7D-9-CV Corsair II, 70-1054, c/n D-200, of the 180th TFG, Ohio Air National Guard, based at Toledo Express Airport, Swanton, Ohio, over the coast of Michigan's Thumb area. He landed in Lake Huron, and was dragged 12 miles in his parachute by winds before being lost and presumed drowned. The jet impacted in a wooded area near Port Hope, Michigan. Rescuers were unable to reach pilot at the speed he was being dragged, and survival was unlikely in the 38-degree water.
- 1989 – An Douglas A-4F Skyhawk—Bureau Number 152101, tail number '2101', c/n 13489, assigned to the US Navy Top Gun school, crashed short of the runaway at NAS Miramar, north of San Diego, California. The cause of the crash was loss of power to the engine. The pilot, Lt. Cmdr. Stanley R. O'Connor, an instructor in the Top Gun school, ejected safely. This airframe had been ordered as the final A-4E but was delivered as the first A-4F model.
- 1986 – First flight of the Fokker F100
- 1979 – First flight of the Piper PA-46
- 1962 – Eastern Air Lines Flight 512, a Douglas DC-7 B, crashes as a result of pilot error during a missed approach at New York's Idlewild Airport; 25 of 51 on board are killed.
- 1961 – Ansett-ANA Flight 325, a Vickers Viscount, crashes into Botany Bay, Australia, 9 min after takeoff, killing all 15 people on board.
- 1958 – Royal Canadian Air Force Sikorsky H-34A Choctaw, 9634, c/n 58-224, one of six on strength, of 111 Communications Unit, crashes this date, stricken 1 December.
- 1953 – A USAF C-119 Flying Boxcar crashes in flames while on approach to Orly Airport, Paris, France, killing all six crew. "French officials said the plane appeared to explode in air moments after it had been given a clearance for its approach to the field. They said [that] six bodies had been recovered from the wreckage. Air Force sources said the plane was manned by a ferry crew from Dover Field, Del. The bodies of five men were pulled from the charred wreckage. A sixth crewmen was found dead in a clump of trees after he had tried unsuccessfully to bail out from about 700 feet. His partially-opened parachute was tangled in branches 40 yards from the crash site."
- 1946 – An Argentine Air Force Vickers VC.1 Viking T-1 crashed at El Palomar, Argentina.
- 1944 – During November, B-29 s raiding Japan have carried an average bombload of 2.6 tons (2,359 kg) per plane. This will almost triple by July 1945.
- 1941 – (November 30-December 4)U. S. Navy patrol aircraft based in the Philippine Islands monitor Japanese naval and shipping activity at Camranh Bay in French Indochina.
- 1941 – Mario de Bernardi flies air mail from Milan to Guidonia Montecelio, Italy, in a Caproni Campini N.1 motorjet-powered aircraft. It is the first time air mail is carried in any form of jet aircraft.
- 1939 – Soviet air raids on Helsinki and Viipuri mark the outbreak of the Winter War.
- 1934 – The record-setting French aviatrix Hélène Boucher dies when the Renault Viva Grand Sport she is piloting on a test flight crashes into the woods at Guyancourt, France.
- 1923 – Second of two prototypes of the Short Springbok Mk. I, J6975, crashes near Martlesham when it spins in shortly after take off, killing the pilot. Cause is diagnosed as rudder blanking during spinning and a new wing design is prepared for the Short Springbok Mk. II, of which six examples - later reduced to three - are ordered in 1924.
- 1917 – First flight of the Vickers Vimy
- 1913 – The first air-to-air dogfight, pilots from rival Mexican factions exchanged revolver shots in the air over Naco, Mexico.
- 1913 – First air-to-air dogfight: pilots (Dean Ivan Lamb) from rival Mexican factions exchanged revolver shots flying a Curtiss Pusher vs Phil Rader in a Christopherson biplane during the Siege of Naco, Mexico. The combat ended with no hits registered.
- 1911 – First Chief of State flying on an airplane: Francisco I. Madero in a Deperdussin, Mexico City
- 1908 – La Compagnie Generale de Navigation Aérienne, the French Wright company, is organized.
- 1907 – Glenn Curtiss founds the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company, the first airplane manufacturing company in the United States.
- 1905 – The Aero Club of America is established in New York City.
- 1905 – Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin's LZ2 airship is damaged while attempting its first launch.
- 1784 – Jean-Pierre Blanchard makes the first scientific observations from above the earth in a hydrogen balloon over London.
References
- 1 2 "Cargo plane crashes into houses in Congo-Brazzaville, killing 32". BNO News. 1 December 2012. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ↑ Simon Hradecky (December 2, 2012). "Crash: Aero Services IL76 at Brazzaville on Nov 30th 2012, impacted buildings short of runway". Aviation Herald. Retrieved December 3, 2012.
- Shortcuts to this page: Portal:Airplanes • P:AVIA




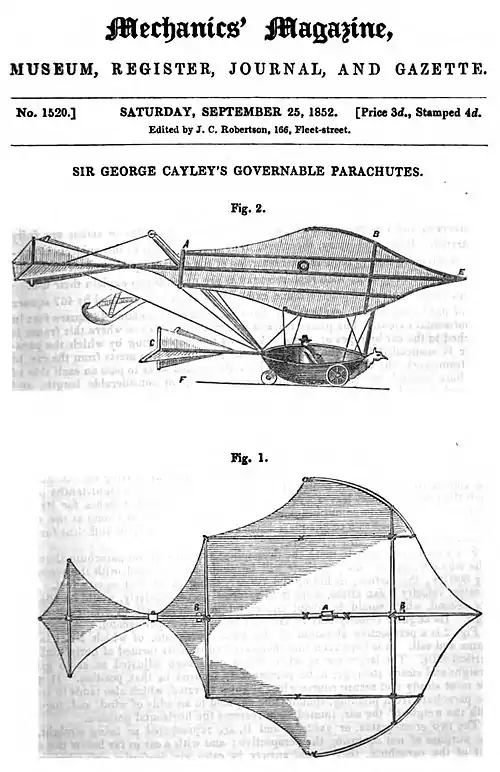


.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
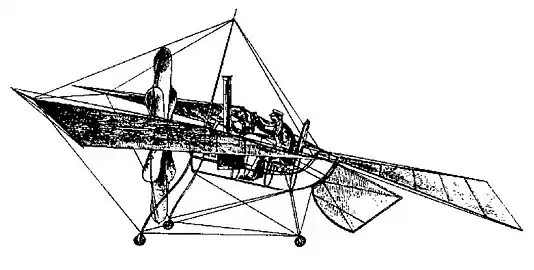









%252C_Netherlands_PP1151411024_(cropped).jpg.webp)


.png.webp)















.jpg.webp)





.jpg.webp)