
.svg.png.webp)
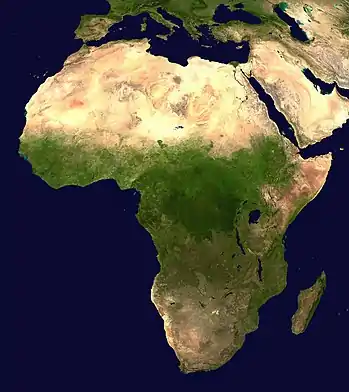
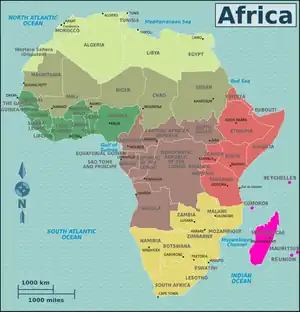
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both aspects. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With 1.4 billion people0 as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context.
Africa straddles the equator and the prime meridian. It is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate to the southern temperate zones. The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere, with a substantial portion and a number of countries in the Southern Hemisphere. Most of the continent lies in the tropics, except for a large part of Western Sahara, Algeria, Libya and Egypt, the northern tip of Mauritania, and the entire territories of Morocco, Ceuta, Melilla, and Tunisia which in turn are located above the tropic of Cancer, in the northern temperate zone. In the other extreme of the continent, southern Namibia, southern Botswana, great parts of South Africa, the entire territories of Lesotho and Eswatini and the southern tips of Mozambique and Madagascar are located below the tropic of Capricorn, in the southern temperate zone.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa also is heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
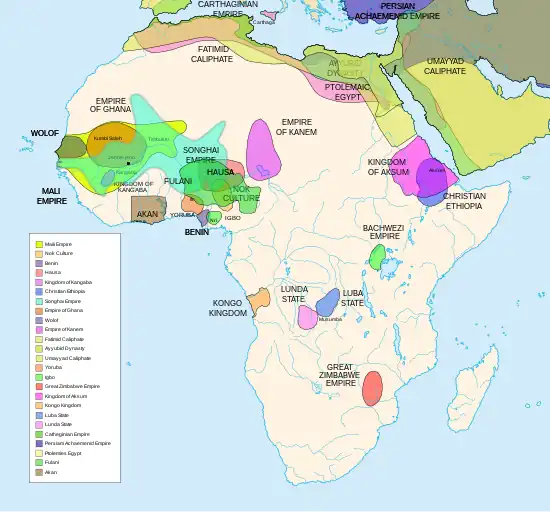
The history of Africa is long, complex, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted as the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade (great apes). The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, including Sahelanthropus tchadensis, Australopithecus africanus, A. afarensis, Homo erectus, H. habilis and H. ergaster—the earliest Homo sapiens (modern human) remains, found in Ethiopia, South Africa, and Morocco, date to circa 233,000, 259,000, and 300,000 years ago, respectively, and Homo sapiens is believed to have originated in Africa around 350,000–260,000 years ago. Africa is also considered by anthropologists to be the most genetically diverse continent as a result of being the longest inhabited. (Full article...)
Selected article –
Tropical Cyclone Elita was an unusual tropical cyclone that made landfall on Madagascar three times. The fifth named storm of the 2003–04 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Elita developed in the Mozambique Channel on January 24, 2004. It strengthened to tropical cyclone status before striking northwestern Madagascar on January 28; it was the first storm to strike western Madagascar at that intensity since Cyclone Cynthia in 1991. Elita weakened to tropical depression status while crossing the island, and after exiting into the southwest Indian Ocean, it turned to the west and moved ashore in eastern Madagascar on January 31. After once again crossing the island, the cyclone reached the Mozambique Channel and re-intensified. Elita turned to the southeast to make its final landfall on February 3 along southwestern Madagascar. Two days later, it underwent an extratropical transition; subsequently, the remnant system moved erratically before dissipating on February 13.
Elita dropped heavy rainfall of more than 200 mm (8 inches), which damaged or destroyed thousands of houses in Madagascar. Over 50,000 people were left homeless, primarily in Mahajanga and Toliara provinces. Flooding from the storm ruined more than 450 km2 (170 sq mi) of agricultural land, including important crops for food. Across the island, the cyclone caused 33 deaths, with its impact further compounded by Cyclone Gafilo about two months later. Elsewhere, Elita brought rainfall and damage to Mozambique and Malawi, and its outer wind circulation produced rough seas and strong gusts in Seychelles, Mauritius, and Réunion. (Full article...)Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -
- ... that Siphesihle November was brought to Canada from South Africa for ballet training at age 11, and became a principal dancer with the National Ballet of Canada at 22?
- ... that despite the United States outlawing slavery in 1865, historian Antoinette Harrell found examples of African-American families who remained enslaved through debt bondage as recently as the 1970s?
- ... that after erecting the African Union headquarters, the Chinese government was accused in 2018 of spying on the building for five years?
- ... that nursing educator Helen Turner Watson was one of the first African-American women to become a commissioned officer in the United States Navy?
- ... that the Enterprise, a black newspaper in Omaha, supported a separate African American department at the 1898 Trans-Mississippi Exposition?
- ... that Rachel Belden Brooks was an African-American pioneer who was awarded $1,000 when she sued the estate of her previous enslaver?
Categories
Selected biography –
Souleymane Bamba (born 13 January 1985) is a former professional footballer who played as a centre-back. He was most recently the first team coach/assistant manager at Cardiff City.
Bamba started his career in his native France with Paris Saint-Germain, but failed to establish himself in their first team. He moved to Scotland to join Dunfermline Athletic in 2006, helping the club reach the final of the Scottish Cup in his first season. Two years later, he was transferred to Hibernian, before joining English side Leicester City in January 2011. (Full article...)Selected country –
 Flag of the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria |
||
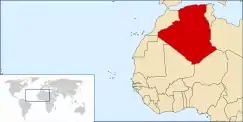 | ||
Algeria (Arabic: الجزائر, Al Jaza'ir, Berber: ![]() , Dzayer [ldzæjər]), officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is the second largest country on the African continent. It is bordered by Tunisia in the northeast, Libya in the east, Niger in the southeast, Mali and Mauritania in the southwest, and Morocco and Western Sahara in the west.
, Dzayer [ldzæjər]), officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is the second largest country on the African continent. It is bordered by Tunisia in the northeast, Libya in the east, Niger in the southeast, Mali and Mauritania in the southwest, and Morocco and Western Sahara in the west.
Algeria is a member of the United Nations, African Union, Arab League and OPEC. Constitutionally, Algeria is defined as an Islamic, Arab, and Amazigh (Berber) country.
The name Algeria is derived from the name of the city of Algiers, from the Arabic word al-jazā’ir, which translates as the islands, referring to the four islands which lay off the city's coast until becoming part of the mainland in 1525. Al-jazā’ir is itself a truncated form of the city's older name jazā’ir banī mazghannā, "the jazeera of (the tribe) Bani Mazghanna", used by early medieval geographers such as al-Idrisi and Yaqut al-Hamawi. (Read more...)
Selected city –
Mogadishu (/ˌmɒɡəˈdiːʃuː, -ˈdɪʃ-/, also US: /ˌmoʊɡ-, ˌmɔːɡ-/; Somali: Muqdisho, Wadaad: مُقْدِشو [mʉq'dɪ:ʃɔ] or Xamar, Wadaad: حَمَرْ [ħɑmɑr]; Arabic: مقديشو, Italian: Mogadiscio), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Ocean for millennia, and has an estimated urban population of 2,610,483. Mogadishu is located in the coastal Banadir region on the Indian Ocean, which unlike other Somali regions, is considered a municipality rather than a maamul goboleed (federal state).
Mogadishu has a long history, which ranges from the ancient period up until the present, serving as the capital of the Sultanate of Mogadishu in the 9th-13th century, which for many centuries controlled the Indian Ocean gold trade and eventually came under the Ajuran Empire in the 13th century which was an important player in the medieval Silk Road maritime trade. Mogadishu enjoyed the height of its prosperity during the 14th and 15th centuries and was during the early modern period considered the wealthiest city on the East African coast, as well as the center of a thriving textile industry.. In the 17th century, Mogadishu and parts of southern Somalia fell under the Hiraab Imamate. In the 19th century it came under the Geledi Sultanate's sphere of influence yet the Abgal imams still held to power within and outside of the city. (Full article...)In the news
- 1 December 2023 – 2023 Malagasy presidential election
- Madagascar's supreme court confirms Andry Rajoelina's election as president after dismissing several challenges against the provisional results. (Reuters)
- 30 November 2023 –
- Gunfire breaks out between the National Guard of Guinea-Bissau and the Presidential Guard after the National Guard frees two ministers from the opposition PAIGC from police custody. (BBC) (Al Jazeera)
- 27 November 2023 – 2023 Africa floods
- The death toll from floods in Kenya rises to 76 as 40,000 people are displaced from their homes. (AP)
- 27 November 2023 – Impala Platinum mine shaft accident
- Eleven workers are killed and 75 others are injured at an Impala platinum mine in Rustenburg, North West, South Africa, when a lift transporting them to the surface drops approximately 200 metres (660 ft). (Al Jazeera)
- 27 November 2023 –
- International Criminal Court Deputy Prosecutor Nazhat Shameem terminates all further investigations into crimes related to the 2007–2008 Kenyan crisis, following the collapse of cases against six suspects, including former and current Presidents Uhuru Kenyatta and William Ruto, due to insufficient evidence and witness tampering. (AFP via VOA)
- 27 November 2023 – 2023 Malagasy presidential election
- Two Madagascar army colonels are detained and charged with inciting mutiny and threatening national security during the election, with allegations of offering bribes to army leaders to destabilize the election results that declared Andry Rajoelina the winner. (AFP via The EastAfrican)
Updated: 21:33, 1 December 2023
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ... that Dutch malacologist Adolph Cornelis van Bruggen is an expert in African land snails?
- ... that a 20‑day study reported by BirdLife International discovered 265 species of birds in Nki National Park?
- ... that Kalulu, an African boy who died in 1877, was modeled in Madame Tussauds and attended Dr. Livingstone's funeral in London?
- ... that Samuel Jackman Prescod became the first person of African descent elected to the Parliament of Barbados?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals

.jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)




_adult_male.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)









.jpg.webp)






_5.png.webp)





.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)






