 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxo(phenyl)acetic acid | |
| Other names
Benzoyl formate Phenylglyoxalic acid Phenylglyoxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.345 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
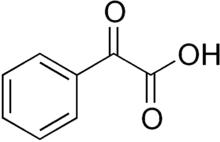
| C8H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 150.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 64 to 66 °C (147 to 151 °F; 337 to 339 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Phenylglyoxylic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CO2H. The conjugate base, known as benzoylformate is the substrate of benzoylformate decarboxylase, a thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzyme:
- benzoylformate + H+ ⇌ benzaldehyde + CO2
It is a colourless solid with a melting point of 64–66 °C and is moderately acidic (pKa = 2.15).
Phenylglyoxylic acid can be synthesized by oxidation of mandelic acid with potassium permanganate.[1] An alternative synthesis involves hydrolysis of benzoyl cyanide.[2]
References
- ↑ B. B. Corson, Ruth A. Dodge, S. A. Harris, and R. K. Hazen (1941). "Ethyl Benzoylformate". Organic Syntheses.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collective Volume, vol. 1, p. 241 - ↑ T. S. Oakwood and C. A. Weisgerber (1955). "Benzoylformic Acid". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 3, p. 114
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.