The Midland Alpine borane reduction, or simply the Midland reduction, is a reagent for the asymmetric reduction of carbonyls (primarily ketones) to alcohols.[1] The synthesis of Alpine borane is well established. Many substrates for the Midland reduction have a low steric group such as an alkyne[2] or a nitrile[3] so as to increase selectivity.
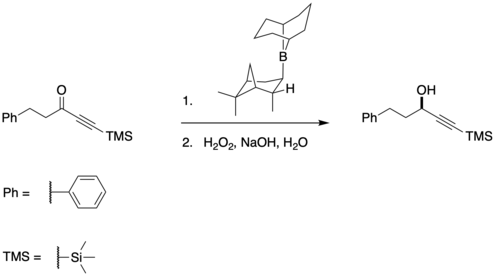
Asymmetric reduction of carbonyls using R-Alpine Borane
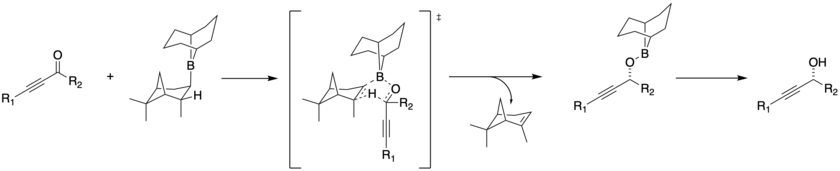
The stereochemical control comes from coordination of the bulky borane to the carbonyl, followed by hydride transfer opposite the largest group.
See also
References
- ↑ Li, J. J. (2009). Name Reactions, A Collection of Detailed Mechanisms and Synthetic Applications (4th ed.). New York, New York: Springer. pp. 359–360. ISBN 978-3-642-01052-1.
- ↑ Intramolecular Arene-Alkyne Photocycloaddition M. C. Pirrung J. Org. Chem.; 1987; 52(8); pp 1635 - 1637; doi:10.1021/jo00384a057
- ↑ M. M. Midland, P. E. Lee J. Org. Chem.; 1985; 50(17); pp 3239 - 3241; doi:10.1021/jo00217a053
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.