| Medial epicondyle of the femur | |
|---|---|
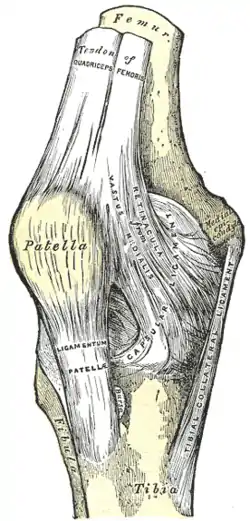 Right knee-joint. Anterior view. (Medial epicondyle visible at right.) | |
 Right femur. Anterior surface. (Medial epicondyle labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | epicondylus medialis femoris |
| TA98 | A02.5.04.022 |
| TA2 | 1381 |
| FMA | 32864 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle, a bony protrusion, located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end.
Located above the medial condyle, it bears an elevation, the adductor tubercle,[1] which serves for the attachment of the superficial part, or "tendinous insertion", of the adductor magnus.[2] This tendinous part here forms an intermuscular septum which forms the medial separation between the thigh's flexors and extensors.[3]
Behind it, and proximal to the medial condyle[4] is a rough impression which gives origin to the medial head of the Gastrocnemius.
See also
Notes
Additional images
 Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view.
Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view. Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view.
Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view. Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view.
Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view. Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view.
Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 247 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 247 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Right femur (anterior - distal end) - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
- Anatomy photo:17:st-0302 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.