| Diphydontosaurus Temporal range: Late Triassic, | |
|---|---|
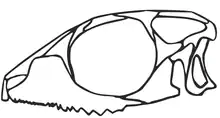 | |
| Skull of D. avonis in lateral view | |
.jpg.webp) | |
| Lombary specimen of Diphydontosaurus sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Rhynchocephalia |
| Genus: | †Diphydontosaurus Whiteside, 1986 |
| Species: | †D. avonis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Diphydontosaurus avonis Whiteside, 1986 | |
Diphydontosaurus is an extinct genus of small rhynchocephalian reptile from the Late Triassic of Europe. It is the most primitive known member of Sphenodontia.
Description
Diphydontosaurus was one of the smallest sphenodontians, measuring up to 10 cm (4 in) long. It had long, sharp claws to help it catch its prey.[1] The skull, which was around 1.4 cm (0.55 in) long, had large orbits (eye sockets), as well as a combination of a majority of frequently replaced conical pleurodont teeth on the front of the jaws and a few permanent acrodont teeth in the posterior jaws. It was likely an insectivore which used its acrodont posterior teeth to dismember prey.[2]
Classification
Diphydontosaurus avonis is known from abundant remains covering most of the skeleton found in fissure fill deposits in Southwest Britain.[1] A skeleton of a juvenile sphenodontian tenatively referred to Diphydontosaurus was reported in 1996 from the Norian of Lombardy in Italy.[3]
In most recent analyses it has been recovered as the most basal sphenodontian.[4]
The following is a cladogram of Rhynchocephalia after DeMar et al. 2022.[5]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleoecology
Diphydontosaurus avonis was a small animal that lived in the Bristol Channel region of England. It lived during the Late Triassic about 205 mya. The deposits in which it is from are complete enough for its ecosystem to be reconstructed in 2012. In the Late Triassic, the regions that Diphydontosaurus lived in were numerous rocky, small caves, that sat on a limestone bed. It is likely that the caves were eroded by possibly acidic rainwater. Diphydontosaurus is very well known from these deposits, potentially because they drowned after a rainstorm or monsoon.[1]
References
Footnotes
- 1 2 3 Benson et al. 2012, pp. 208–209.
- ↑ "The head skeleton of the Rhaetian sphenodontid Diphydontosaurus avonis gen. et sp.nov. and the modernizing of a living fossil". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences. 312 (1156): 379–430. 1986-05-19. doi:10.1098/rstb.1986.0014. ISSN 0080-4622.
- ↑ Renesto, S., 1995, A sphenodontid from the Norian (Late Triassic) of Lombardy (Northern Italy): a preliminary note: Modern Geology, v. 20, p. 149–158.
- ↑ Rauhut et al. 2012.
- ↑ DeMar, David G.; Jones, Marc E. H.; Carrano, Matthew T. (2022-12-31). "A nearly complete skeleton of a new eusphenodontian from the Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation, Wyoming, USA, provides insight into the evolution and diversity of Rhynchocephalia (Reptilia: Lepidosauria)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 20 (1): 1–64. doi:10.1080/14772019.2022.2093139. hdl:2440/136608. ISSN 1477-2019. S2CID 252325953.
Citations
- Benson, R.; Brusatte, S.; Hone, D.; Naish, D.; Xu, X.; Anderson, J.; Clack, J.; Duffin, C.; Milner, A.; Parsons, K.; Prothero, D.; Johanson, Z.; Dennis-Bryan, K. (2012) [2009]. Ambrose, Jamie; Gilpin, David; Hirani, Salima; Jackson, Tom; Joyce, Nathan; Maiklem, Lara; Marriott, Emma; Nottage, Claire; van Zyl, Meizan (eds.). Prehistoric Life: A Definitive Visual History of Life on Earth. Dorling Kindersley. pp. 1–512. ISBN 978-0-7566-9910-9. OCLC 444710202.
- Rauhut, O. W. M.; Heyng, A. M.; López-Arbarello, A.; Hecker, A. (2012). "A new rhynchocephalian from the Late Jurassic of Germany with a dentition that is unique amongst tetrapods". PLOS ONE. 7 (10): e46839. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...746839R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046839. PMC 3485277. PMID 23118861.
- Whiteside DI (1986). "The head skeleton of the Rhaetian sphenodontid Diphydontosaurus avonis gen. et sp. nov., and the modernising of a living fossil". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 312 (1156): 379–430. Bibcode:1986RSPTB.312..379W. doi:10.1098/rstb.1986.0014.
- Jones, MEH (2008). "Skull shape and feeding strategy in Sphenodon and other Rhynchocephalia (Diapsida: Lepidosauria)". Journal of Morphology. 269 (8): 945–966. doi:10.1002/jmor.10634. PMID 18512698.
- Whiteside, DI; Marshall, JEA (2008). "The age, fauna and palaeoenvironment of the Late Triassic fissure deposits of Tytherington, South Gloucestershire, UK". Geological Magazine. 145 (1): 105–147. Bibcode:2008GeoM..145..105W. doi:10.1017/S0016756807003925. S2CID 129614690.