| Battle of St. Pölten | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the War of Austrian Succession | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 40,000 | 22,000 | ||||||
The Battle of St. Pölten was a decisive engagement between Austrian and Franco-Bavarian forces, which had a significant impact on the procession of the 1741 Austrian campaign.
Background
In 1740, Frederick the Great launched an invasion of Silesia and emerged victorious against the Austrians at the Battle of Mollwitz.[1] Initially, the Habsburg Monarchy was governed by the Salic Law, which excluded women from inheritance. However, the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 lifted this restriction, paving the way for Maria Theresa to succeed her father on the throne.[2] However, it became clear that Austria lacked the strength to defend all of its territories. As a result, several European countries entered into an agreement called the League of Nymphenburg to divide and dismantle Austria's territories.[3]
The situation was grim for Austria, as French and Bavarian troops invaded Upper Austria, while 20,000 Saxons simultaneously invaded Bohemia.[4]
In late November 1741, 10,000 Spanish soldiers landed at Orbitello, followed by 16 more battalions at Lerici and La Spezia. Expecting a dozen more battalions and 4,500 horses, Austrian commander Otto Ferdinand von Traun was left with only 9,500 infantry and 2,400 cavalry to face over 26,000 Spanish and Neapolitan soldiers.Sardinia, as a member of the League of Nymphenburg, could potentially invade Austrian Lombardy, while the Duke of Modena could join the opposing side.[5]
Battle
While Vienna was under military detention, a significant number of troops quickly gathered in the neighboring regions of Hungary and Croatia to provide aid. The enemy became aware of this and imposed a siege on Vienna, which had probably been planned since the beginning of the war. The situation seemed hopeless, and Maria Theresa left Vienna for Pressburg and then Budapest, where the estates from all over Hungary gathered. With tears streaming down her face, she watched the spectacle unfold around her, and the Hungarians shouted their determination to come to their aid as quickly as possible. At first, only 22,000 of the 60,000 troops could be called up. But Khevenhüller assured Maria Theresa that it would be enough to drive out the invaders.[6]
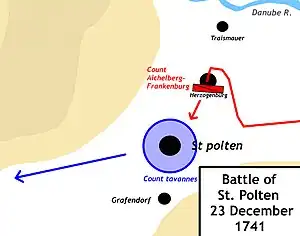
The Hungarian cavalry, led by Khevenhüller, appeared shortly after the French had assembled in St. Pölten on 23 December 1741. The Hungarians entered the St. Pölten area in a roundabout way and unexpectedly in the middle of the night from Herzogenburg. They cleverly surprised the French and launched a swift attack on the enemy camp. After defeating several French soldiers, the Hungarian cavalry attacked Count Tavannes, a nobleman, and a group of regular French soldiers at noon. News of the skirmish spread quickly throughout the city and camp, causing great consternation and confusion. The city gates were immediately closed by the guards, while regiments armed themselves and prepared to engage the Hungarians. Meanwhile, however, Khevenhüller's junior officer, Menzel, oversaw the Hungarians and the booty, all without casualties.
On this occasion, a significant disparity was observed between the Hungarian and French cavalry. Although both armies were organized into squadrons, the resulting battle revealed the superiority of the Hungarian cavalry over the French. Tavannes was subsequently captured and taken to Vienna. Although highly regarded by the Bavarian elector, he was quickly released from captivity. The battle finally ended with the French retreating from St. Pölten.[7]
Aftermath
The battle turned the war in Austria's favor. On 17 January 1742, Khevenhüller defeated a Bavarian army at Schärding; a week later, 10,000 French soldiers surrendered after a brief battle at Linz. Although Charles Albert of Bavaria was crowned as Charles VII, the next Holy Roman Emperor and the first non-Habsburg to ascend the throne in 300 years, the Bavarian capital of Munich was taken at the same time.
In addition, Count Otto Ferdinand von Traun, the Austrian commander, marched ahead of the 40,000-strong Spanish-Neapolitan army, took Modena, and forced the Duke to agree to a separate peace.[8] On 1 February 1742, Schulenburg and Ormea signed the Convention of Turin, which settled (or postponed) many differences and established an alliance between the two countries, with Sardinia officially changing sides.[9]
However, Frederick the Great once again emerged victorious over the Austrians at the Battle of Chotusitz. He then signed the Treaty of Breslau, which acknowledged the humiliating permanent loss of Silesia to Prussia.[10]
References
- ↑ Longman 1895, p. 117; Pratt 1956, p. 209.
- ↑ Anderson 1995, p. 3.
- ↑ Clark 2006, pp. 193–194.
- ↑ Asprey 1986, p. 223.
- ↑ Von Duncker, Carl (1894). Abensberg und Traun, Otto Ferdinand Graf von. Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie. Carl von Duncker. p. 509.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ↑ Anderson 1995, p. 86.
- ↑ SCHWERDFEGER, JOSEF. DIE AUFZEICHNUNGEN DBS ST. PÖLTENER CHORHERRN AQUILIN JOSEPH HACKER ÜBER DEN EINFALL KARLS VII. (KARL ALBRECHTS) IN ÖSTERREICH, 1741 BIS 1742. JOSEF SCHWERDFEGER.
- ↑ Hannay 1911, p. 40.
- ↑ Browning 2005, p. 97.
- ↑ Showalter 2012, p. 27.
Sources
- Anderson, Mark (1995). "The Prussian Invasion of Silesia and the Crisis of Habsburg Power". The War of the Austrian Succession. Routledge. ISBN 978-0582059504.
- Asprey, Robert B. (1986). "The First Silesian War, 1740-1742". Frederick the Great: The Magnificent Enigma. New York: Ticknor and Fields. ISBN 978-0-89919-352-6.
 (registration required)
(registration required) - Browning, Reed (2005). "New Views on the Silesian Wars". The Journal of Military History. 69 (2): 521–534. doi:10.1353/jmh.2005.0077. JSTOR 3397409. S2CID 159463824.
 (registration required)
(registration required) - Clark, Christopher (2006). "Struggle for Mastery". Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600–1947. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Belknap Press. ISBN 978-0-674-02385-7.
 (registration required)
(registration required) - This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Hannay, David (1911). "Austrian Succession, War of the". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 3 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 39–45.
- Longman, Frederick (1895). "The Conquest of Silesia". Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' War. F. W. Longman.
- Pratt, Fletcher (1956). "Frederick the Great and the Unacceptable Decision". The Battles that Changed History: From Alexander the Great to Task Force 16. Garden City, NY: Hanover House.
 (registration required)
(registration required) - Showalter, Dennis (2012). Frederick the Great: A Military History. Frontline Books. ISBN 978-1848326408.