 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methylbutanedioic acid | |
| Other names
Pyrotartaric acid; 2-Methylbutanedioic acid; Propane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.144 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 132.115 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 117.5 °C (243.5 °F; 390.6 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
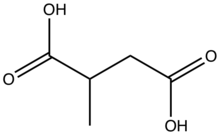
2-Methylsuccinic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH(CH3)CH2CO2H. A white solid, it is the simplest chiral dicarboxylic acid. It is a recurring component of urban aerosols.[1] Salts and esters of 2-methylsuccinic acid are called 2-methylsuccinates.
Preparation
It can be prepared by partial hydrogenation of itaconic acid over Raney nickel.[2] Alternatively, hydrocyanation of ethyl crotonate affords an intermediate, which converts to 2-methylsuccinic acid after hydrolysis of the ester and nitrile substituents.[3]
References
- ↑ Kawamura, Kimitaka; Ikushima, Kouichi (1993). "Seasonal Changes in the Distribution of Dicarboxylic Acids in the Urban Atmosphere". Environmental Science and Technology. 27: 2227–35. doi:10.1021/es00047a033.
- ↑ R. F. Feldkamp; B. F. Tullar (1954). "3-Methylthiophene". Org. Synth. 34: 73. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.034.0073.
- ↑ George Bosworth Brown (1946). "Methylsuccinic acid". Org. Synth. 26: 54. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.026.0054.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.