Pangaea
English
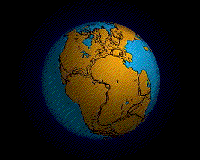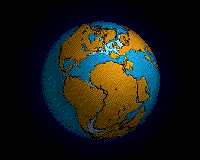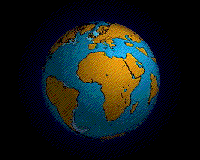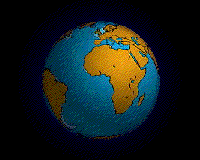
The breakup of Pangaea.
Etymology
From Ancient Greek παν- (pan-, “all”) + γαῖα (gaîa, “earth, land”), after German Pangäa, which was coined by Alfred Wegener in 1915. Analyzable as pan- + Gaea
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /pænˈd͡ʒiː.ə/, enPR: păn-jēʹə
- Hyphenation: pan‧gae‧a
Audio (Southern England) (file)
Proper noun
Pangaea
- (geology) A supercontinent that included all the landmasses of the earth before the Triassic period and that broke up into Laurasia and Gondwana.
- 2021, J. B. Murphy, R. A. Strachan, C. Quesada, editors, Pannotia to Pangaea […] , Geological Society of London, →ISBN, page 82:
- The supercontinent status of Pangaea and Rodinia is undisputed. In contrast, there is ongoing controversy on whether Pannotia existed at all.
Derived terms
- Neopangaea, Neopangea
- New Pangaea, New Pangea
- Novopangaea, Novopangea
- Pangaea II, Pangea II
- Pangaean, Pangean
- Pangaea Next, Pangea Next
- Pangaea Proxima, Pangea Proxima
- Pangaea Ultima, Pangea Ultima
- Urpangaea, Urpangea
Translations
supercontinent prior to Triassic
|
See also
Anagrams
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.