Welcome to the shark portal

Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorpha (or Selachii) and are the sister group to the Batoidea (rays and kin). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as Cladoselache and Doliodus first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The oldest modern sharks (selachimorphs) are known from the Early Jurassic, about 200 million years ago.
Sharks range in size from the small dwarf lanternshark (Etmopterus perryi), a deep sea species that is only 17 centimetres (6.7 in) in length, to the whale shark (Rhincodon typus), the largest fish in the world, which reaches approximately 12 metres (40 ft) in length. They are found in all seas and are common to depths up to 2,000 metres (6,600 ft). They generally do not live in freshwater, although there are a few known exceptions, such as the bull shark and the river shark, which can be found in both seawater and freshwater. Sharks have a covering of dermal denticles that protects their skin from damage and parasites in addition to improving their fluid dynamics. They have numerous sets of replaceable teeth.
Several species are apex predators, which are organisms that are at the top of their food chain. Select examples include the tiger shark, blue shark, great white shark, mako shark, thresher shark, and hammerhead shark. (Full article...)
Selected article -

A slow-moving predator feeding mainly on bony fishes, the sicklefin lemon shark seldom travels long distances and many individuals can be found year-round at certain locations. Like other members of its family, this species is viviparous with females giving birth to as many as 13 pups every other year, following a gestation period of 10–11 months. Although they are potentially dangerous to humans and known to respond vigorously to any provocation, under normal circumstances sicklefin lemon sharks are cautious and tend to retreat if approached. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed this species as Vulnerable; its low reproductive productivity and rate of movement limits the capacity of depleted stocks to recover. Off India and Southeast Asia, this species has been severely depleted or extirpated by unregulated exploitation for its meat, fins, and liver oil.
Did you know (auto-generated)
- ... that since 2018, IKEA's stuffed toy shark Blåhaj has become a popular Internet meme and an icon of the online transgender community?
- ... that "the Hurricane Shark is real"?
- ... that Timo Meier became the first player in San Jose Sharks franchise history to score five goals in one game when he was 25?
- ... that Alexis Sharkey's last Instagram post before her murder documented her travels to Tulum, Mexico?
- ... that Hixxy and Sharkey created a schism in the UK rave music scene in 1995?
- ... that the ampullae of Lorenzini enable sharks to sense electric fields?
Categories
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects related to sharks:
- WikiProject Science
- WikiProject Biology
- WikiProject Tree of Life
- WikiProject Animals
- WikiProject Fishes
- WikiProject Sharks
- WikiProject Fishes
- WikiProject Animals
- WikiProject Tree of Life
- WikiProject Biology
- WikiProject Aquarium Fishes
- WikiProject Fishing
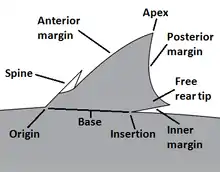
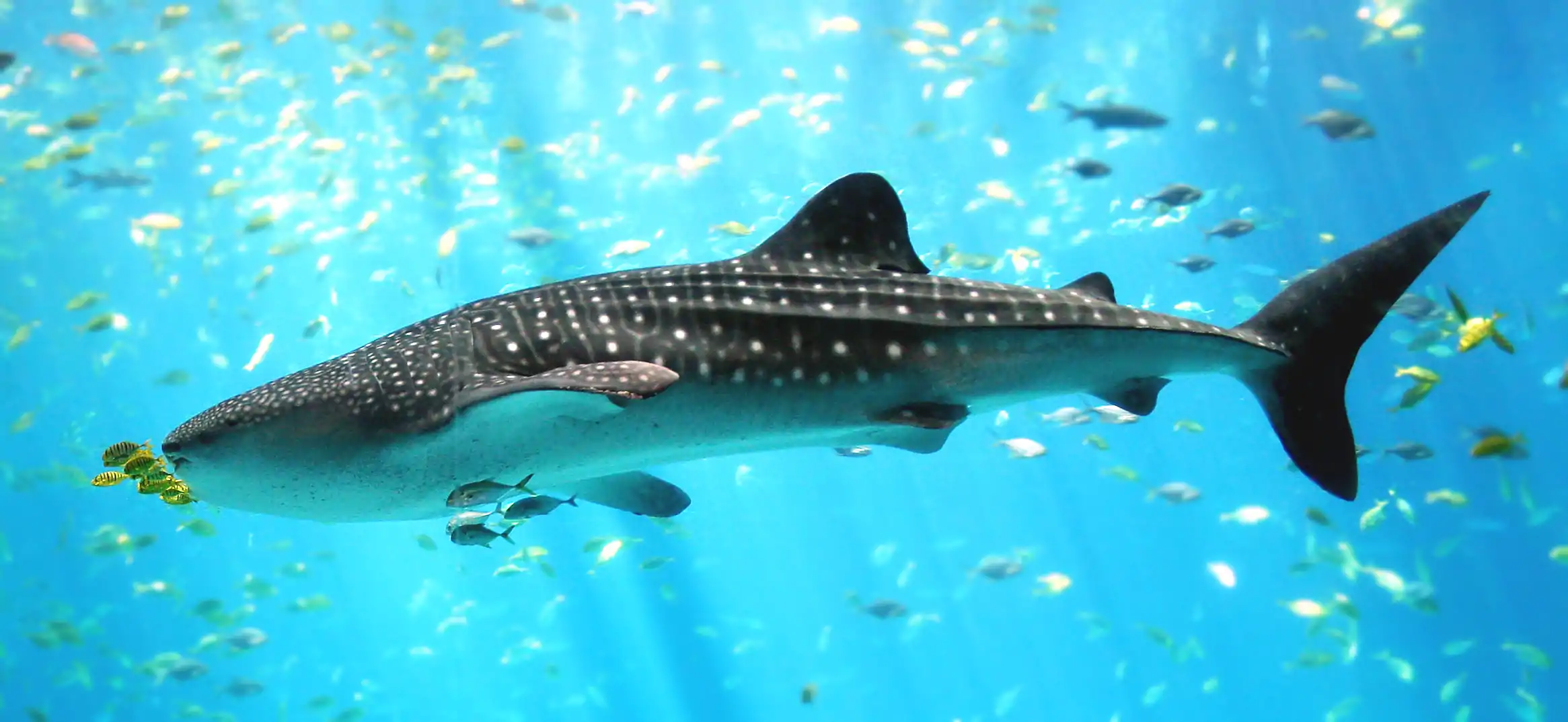
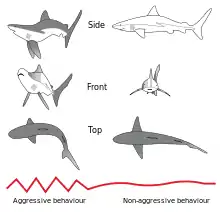
Selected picture -
.jpg.webp)
More Did you know? -
- ... that the spadenose shark exhibits the most advanced form of placental reproduction in fishes?
- ... that the dark, puffadder, brown, and Natal shysharks of South Africa are so named because they curl into a ring when threatened and "shyly" cover their eyes with their tails?
- ... that the daggernose shark can adjust the timing of events in its reproductive cycle by several months?
- ... that the lollipop catshark is shaped like a tadpole and has an almost gelatinous body?
- ... that the Australian swellshark can survive out of water for more than a day?
General images
Topics
 See also
See also 
For additional lists of marine life-related featured articles and good articles see:
- WikiProject Cetaceans § Featured and Good Content
- Portal:Fish/Recognized content
- Portal:Marine life/Recognized content
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals

.jpg.webp)







_(46722837981).jpg.webp)



