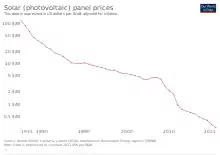
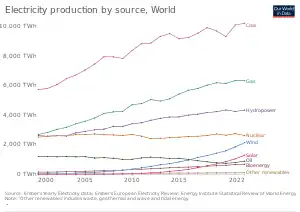
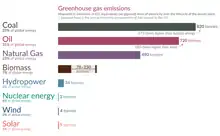
Introduction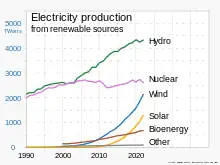 Renewable energy sources, especially solar photovoltaic and wind, are providing an increasing share of electricity production. Renewable energy is energy from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. Renewable resources include sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. Renewable energy is often used for electricity generation, heating and cooling. Renewable energy projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification, which has several benefits: electricity can move heat or objects efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. From 2011 to 2021, renewable energy grew from 20% to 28% of global electricity supply. Use of fossil energy shrank from 68% to 62%, and nuclear from 12% to 10%. The share of hydropower decreased from 16% to 15% while power from sun and wind increased from 2% to 10%. Biomass and geothermal energy grew from 2% to 3%. There are 3,146 gigawatts installed in 135 countries, while 156 countries have laws regulating the renewable energy sector. In 2021, China accounted for almost half of the global increase in renewable electricity. Globally there are over 10 million jobs associated with the renewable energy industries, with solar photovoltaics being the largest renewable employer. Renewable energy systems are rapidly becoming more efficient and cheaper and their share of total energy consumption is increasing, with a large majority of worldwide newly installed electricity capacity being renewable. In most countries, photovoltaic solar or onshore wind are the cheapest new-build electricity. Many nations around the world already have renewable energy contributing more than 20% of their total energy supply, with some generating over half their electricity from renewables. A few countries generate all their electricity using renewable energy. National renewable energy markets are projected to continue to grow strongly in the 2020s and beyond. According to the IEA, to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, 90% of global electricity generation will need to be produced from renewable sources. Some studies have shown that a global transition to 100% renewable energy across all sectors – power, heat, transport and industry – is feasible and economically viable. Renewable energy resources exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to fossil fuels, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Deployment of renewable energy and energy efficiency technologies is resulting in significant energy security, climate change mitigation, and economic benefits. However renewables are being hindered by hundreds of billions of dollars of fossil fuel subsidies. In international public opinion surveys there is strong support for renewables such as solar power and wind power. In 2022 the International Energy Agency asked countries to solve policy, regulatory, permitting and financing obstacles to adding more renewables, to have a better chance of reaching net zero carbon emissions by 2050. (Full article...) Selected article -Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic effect. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight to a hot spot, often to drive a steam turbine. Photovoltaics were initially solely used as a source of electricity for small and medium-sized applications, from the calculator powered by a single solar cell to remote homes powered by an off-grid rooftop PV system. Commercial concentrated solar power plants were first developed in the 1980s. Since then, as the cost of solar electricity has fallen, grid-connected solar PV systems' capacity and production have grown more or less exponentially, doubling about every three years. Millions of installations and gigawatt-scale photovoltaic power stations continue to be built, with half of new generation capacity being solar in 2021. In 2022 solar generated 4.5% of the world's electricity, compared to 1% in 2015 when the Paris Agreement to limit climate change was signed. Along with onshore wind, in most countries the cheapest levelised cost of electricity for new installations is utility-scale solar. (Full article...)Quotations -
Main topicsRenewable energy sourcesGeneralRenewable energy commercialization · Smart grid · Timeline of sustainable energy research 2020–present Renewable energy by countryList of countries by electricity production from renewable sources
WikiProjectsWikiProjects connected with renewable energy:
Selected image - Rapeseed field at Grendon, Northamptonshire. Rapeseed oil is used in the manufacture of biodiesel for powering motor vehicles. Selected biography - Prof. Stefan Krauter (2015) Did you know? -... that the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation (SRREN) in May 2011 ? The IPCC examined renewable energy and energy efficiency in its fourth assessment report, published in 2007, but members have now decided that renewable energy commercialization merits in-depth coverage because of its importance in reducing carbon emissions. General images -The following are images from various renewable energy-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsCategoriesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Renewable energy Renewable energy by continent Renewable energy by country Lists related to renewable energy Algaculture Anaerobic digestion Bioenergy Renewable energy certification Documentary films about alternative energy Geothermal energy Renewable energy organizations People associated with renewable energy Renewable energy policy Renewable electricity Renewable energy economy Solar energy Renewable energy technology Water power Wind power Renewable energy stubs Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|


















![Image 21Concentrated solar panels are getting a power boost. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) will be testing a new concentrated solar power system – one that can help natural gas power plants reduce their fuel usage by up to 20 percent.[needs update] (from Solar energy)](../I/Photo_of_the_Week-_Boosting_Solar_Technology_(8722948189).jpg.webp)