|
The Palaeontology Portal
Introduction A paleontologist at work at John Day Fossil Beds National Monument Paleontology (/ˌpeɪliɒnˈtɒlədʒi, ˌpæli-, -ən-/), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term has been used since 1822 formed from Greek παλαιός ('palaios', "old, ancient"), ὄν ('on', (gen. 'ontos'), "being, creature"), and λόγος ('logos', "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but it differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, nearly 4 billion years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates. (Full article...) Selected article on the prehistoric world and its legacies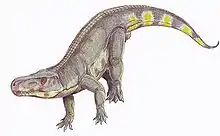 Artist's reconstruction of Batrachotomus. The locality where Batrachotomus lived was a swampy region and the name comes from the Greek batrachos/βάτραχος (frog) and tome/τομή (cutting, slicing), which refers to its preying on the large amphibian Mastodonsaurus. In contrast with sprawling reptiles, like crocodiles, this large carnivore was very agile with locomotor superiority due to its erect stance. A remarkable feature seen on its back was a row of paired, flattened bony plates. Batrachotomus was possibly an early relative of Postosuchus, which lived during the dawn of the dinosaurs. (see more...) Did you know? A life restoration of stag-moose with a human to scale
 Franz Hilgendorf
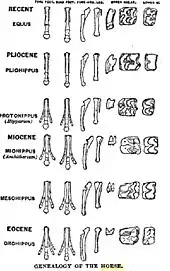
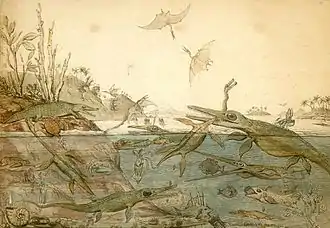
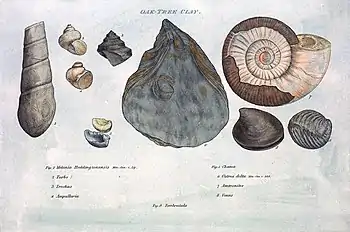
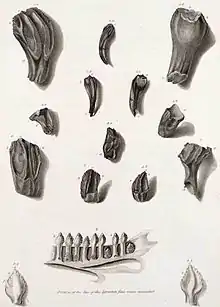
General images -The following are images from various paleontology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected article on paleontology in human science, culture and economics Portrait of Mary Anning Mary Anning searched for fossils in the area's Blue Lias cliffs. Her discoveries included the first ichthyosaur skeleton correctly identified; the first two plesiosaur skeletons found; the first pterosaur skeleton located outside Germany; and important fish fossils. Her observations played a key role in the discovery that coprolites, known as bezoar stones at the time, were fossilised faeces. She also discovered that belemnite fossils contained fossilised ink sacs like those of modern cephalopods. Anning did not fully participate in the scientific community of 19th-century Britain, who were mostly Anglican gentlemen. She struggled financially for much of her life. Her family was poor, and her father, a cabinetmaker, died when she was eleven. She became well known in geological circles in Britain, Europe, and America. Nonetheless, as a woman, she was not eligible to join the Geological Society of London and she did not always receive full credit for her scientific contributions. After her death in 1847, her unusual life story attracted increasing interest. (see more...) On this day...November 24:
Is Torosaurus Triceratops? Geometric Morphometric Evidence of Late Maastrichtian Ceratopsid Dinosaurs Leonardo Maiorino, Andrew A. Farke, Tassos Kotsakis, Paolo Piras published 26 Nov 2013 Selected image
CategoriesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Paleontology Paleontology by country Subfields of paleontology Paleontology awards Paleontology in the Caribbean Paleontological concepts and hypotheses Economic paleontology Evolution of the biosphere Fossil record History of paleontology Paleontological institutions and organizations Prehistoric life Paleontology lists Paleontology mass media Paleontological sites Paleontologists Paleontology by year Paleontology stubs TopicsGeneral - Paleontology - Fossil - Evolution - Extinction Quality ContentFeatured paleontology articles
- Achelousaurus
- Acrocanthosaurus
- Albertosaurus
- Allosaurus
- Amargasaurus
- Ankylosaurus
- Apatosaurus
- Archaeopteryx
- Baryonyx
- Carnotaurus
- Catopsbaatar
- Ceratosaurus
- Chicxulub Crater
- Compsognathus
- Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event
- Daspletosaurus
- Deinocheirus
- Deinonychus
- Deinosuchus
- Dilophosaurus
- Dinosaur
- Diplodocus
- Dromaeosauroides
- Edmontosaurus
- Elasmosaurus
- Giganotosaurus
- Gorgosaurus
- Herrerasaurus
- Iguanodon
- Istiodactylus
- Lambeosaurus
- List of dinosaur genera
- Majungasaurus
- Massospondylus
- Megalodon
- Nemegtomaia
- Nigersaurus
- Opisthocoelicaudia
- Paranthodon
- Parasaurolophus
- Plateosaurus
- Psittacosaurus
- Seorsumuscardinus
- Spinosaurus
- Stegosaurus
- Stegoceras
- Styracosaurus
- Tarbosaurus
- Thescelosaurus
- Triceratops
- Tyrannosaurus
- Velociraptor
Things you can do
Current Paleontology FACs - None yet... WikiProjects
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|