The New York State portal

New York, sometimes called New York State, is a state in the Northeastern United States. A Mid-Atlantic state, New York borders New England, and has an international border with Canada. With almost 19.7 million residents, it is the fourth-most populous state in the United States and seventh-most densely populated as of 2022. New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area, with a total area of 54,556 square miles (141,300 km2).
New York has a varied geography. The southeastern part of the state, known as Downstate, encompasses New York City, the most populous city in the United States, Long Island, the most populous island in the United States, and the lower Hudson Valley. These areas are part of the New York metropolitan area, a sprawling urban landmass, and account for approximately two-thirds of the state's population. The much larger Upstate area spreads from the Great Lakes to Lake Champlain, while its Southern Tier region extends to the border of Pennsylvania. Upstate includes the Adirondack Mountains and the Catskill Mountains (part of the wider Appalachian Mountains). The east–west Mohawk River Valley bisects the more mountainous regions, and flows into the north–south Hudson River valley near the state capital of Albany. Western New York, home to the cities of Buffalo and Rochester, is part of the Great Lakes region and borders Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. Central New York is anchored by the city of Syracuse; between the central and western parts of the state, New York is dominated by the Finger Lakes, a popular tourist destination.
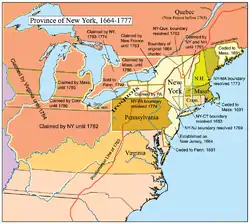
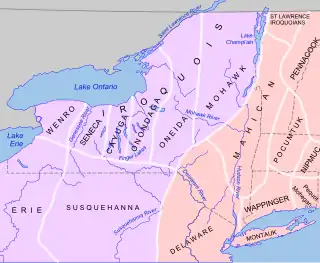
New York was one of the original Thirteen Colonies that went on to form the United States. The area of present-day New York had been inhabited by tribes of the Algonquians and the Iroquois Confederacy Native Americans for several thousand years by the time the earliest Europeans arrived. Stemming from Henry Hudson's expedition in 1609, the Dutch established the multiethnic colony of New Netherland in 1621, which included the settlements of Fort Orange (present-day Albany), Wiltwijck (present-day Kingston), and New Amsterdam (present-day New York City). England seized the colony from the Dutch in 1664, renaming it the Province of New York. (Full article...)
 Good article -
Good article -

Selected article -
Schenectady (/skəˈnɛktədi/) is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-most populous city and the twenty-fifth most-populous municipality by population. The city is in eastern New York, near the confluence of the Mohawk and Hudson rivers. It is in the same metropolitan area as the state capital, Albany, which is about 15 miles (24 km) southeast.
Schenectady was founded on the south side of the Mohawk River by Dutch colonists in the 17th century, many of whom came from the Albany area. The name "Schenectady" is derived from the Mohawk word skahnéhtati, meaning "beyond the pines" and used for the area around Albany, New York. Residents of the new village developed farms on strip plots along the river. Connected to the west by the Mohawk River and Erie Canal, Schenectady developed rapidly in the 19th century as part of the Mohawk Valley trade, manufacturing, and transportation corridor. By 1824, more people worked in manufacturing than agriculture or trade; like many New York cities, it had a cotton mill that processed cotton from the Deep South. In the 19th century, nationally influential companies and industries developed in Schenectady, including General Electric and American Locomotive Company (ALCO), which were powers into the mid-20th century. Schenectady was part of emerging technologies, with GE collaborating in the production of nuclear-powered submarines and, in the 21st century, working on other forms of renewable energy. (Full article...)General images
Selected quote -
 Featured article -
Featured article -

William Henry Seward (/ˈsuːərd/; May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined opponent of the spread of slavery in the years leading up to the American Civil War, he was a prominent figure in the Republican Party in its formative years, and was praised for his work on behalf of the Union as Secretary of State during the Civil War. He also negotiated the treaty for the United States to purchase the Alaska Territory.
Seward was born in 1801 in the village of Florida, in Orange County, New York, where his father was a farmer and owned slaves. He was educated as a lawyer and moved to the Central New York town of Auburn. Seward was elected to the New York State Senate in 1830 as an Anti-Mason. Four years later, he became the gubernatorial nominee of the Whig Party. Though he was not successful in that race, Seward was elected governor in 1838 and won a second two-year term in 1840. During this period, he signed several laws that advanced the rights of and opportunities for black residents, as well as guaranteeing jury trials for fugitive slaves in the state. The legislation protected abolitionists, and he used his position to intervene in cases of freed black people who were enslaved in the South. (Full article...)Selected picture -
Agriculture is a driving force in the economy of upstate New York and New York in general. 35,600 farms occupy 7.55 million acres (31,000 km²), which makes up about 25 percent of the land in the state. Farms in New York produced $3.4 billion in agricultural products in 2001 and New York is the largest producer of cabbage in the United States. New York is an agricultural leader and is one of the top five states in the production of such agricultural products as dairy, apples, cherries, cabbages, potatoes, onions, and maple syrup. This example is a dairy farm in Brunswick, Rensselaer County.
In the news

- June 16: Wikinews interviews candidate for New York City mayor Vitaly Filipchenko
- August 13: Water main bursts in White Plains, New York, US
- June 19: On the campaign trail in the USA, May 2020
- February 15: California lawyer Michael Avenatti convicted of attempted extortion
- October 17: Hundreds arrested for 'dark web' child porn by international task force
- October 10: U.S. judge orders release of President Trump's tax records, appeals court issues delay
- September 29: Fiancée of murdered Saudi journalist demands justice at UN General Assembly
- September 21: NYC Mayor de Blasio ends US presidential campaign
Did you know? -

- ...that the Adirondack Park Agency was created in an attempt to settle the dispute over whether wilderness within the site should be preserved, or be exploited for profit?
- ...that Same-sex marriage in New York became legal on July 24, 2011, under the Marriage Equality Act?
- ...that Coney Island in southern Brooklyn has a population of 60,000?
December selected anniversaries

- Monroe Leland Hayward (December 22, 1840 in Willsboro, New York – December 5, 1899) was a Senator from Nebraska.
- Ronnie Cuber (born December 25, 1941 in New York City) is primarily a jazz baritone saxophonist; he has also played in Latin, pop, rock and blues sessions.
- William Francis Deegan (December 28, 1882 – April 3, 1932) was an architect, Major in the Army Corps of Engineers, and Democratic political leader in New York City.
- Joel Collier (born December 25, 1963 in Buffalo, New York) is a former American football defensive backs coach in the National Football League.
Selected panorama -
Ellis Island, at the mouth of the Hudson River in New York Harbor, is the location of what was at one time the main entry facility for immigrants entering the United States; the facility operated from January 1, 1892 until November 12, 1954. It is owned by the Federal government and is now part of the Statue of Liberty National Monument, under the jurisdiction of the US National Park Service. It is situated in New York City and Jersey City, New Jersey.
Topics
Categories
Recognized content
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject New York (state)}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
Featured articles
 55 Wall Street
55 Wall Street December 1969 nor'easter
December 1969 nor'easter Christmas 1994 nor'easter
Christmas 1994 nor'easter 2006 Westchester County tornado
2006 Westchester County tornado 2009 International Bowl
2009 International Bowl 2009 New York's 20th congressional district special election
2009 New York's 20th congressional district special election Aaliyah
Aaliyah Albany Charter half dollar
Albany Charter half dollar American Airlines Flight 11
American Airlines Flight 11 Art Deco architecture of New York City
Art Deco architecture of New York City Chester A. Arthur
Chester A. Arthur Tropical Storm Barry (2007)
Tropical Storm Barry (2007) Battle of Ticonderoga (1759)
Battle of Ticonderoga (1759) Moe Berg
Moe Berg Briarcliff Manor, New York
Briarcliff Manor, New York David Hillhouse Buel (priest)
David Hillhouse Buel (priest) Mariah Carey
Mariah Carey The Cat and the Canary (1927 film)
The Cat and the Canary (1927 film) Frances Cleveland
Frances Cleveland Grover Cleveland
Grover Cleveland Stephen Crane
Stephen Crane Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore Eunice Newton Foote
Eunice Newton Foote Joseph B. Foraker
Joseph B. Foraker Fort Ticonderoga
Fort Ticonderoga Horace Greeley
Horace Greeley Jake Gyllenhaal
Jake Gyllenhaal Maggie Gyllenhaal
Maggie Gyllenhaal Here Is Mariah Carey
Here Is Mariah Carey Philip Seymour Hoffman
Philip Seymour Hoffman Hudson Sesquicentennial half dollar
Hudson Sesquicentennial half dollar Hudson Valley Rail Trail
Hudson Valley Rail Trail Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson James II of England
James II of England Derek Jeter
Derek Jeter Joppenbergh Mountain
Joppenbergh Mountain Sandy Koufax
Sandy Koufax Ursula K. Le Guin
Ursula K. Le Guin Live and Let Die (novel)
Live and Let Die (novel) Low Memorial Library
Low Memorial Library 1955 MacArthur Airport United Air Lines crash
1955 MacArthur Airport United Air Lines crash John McGraw
John McGraw Assassination of William McKinley
Assassination of William McKinley New Rochelle 250th Anniversary half dollar
New Rochelle 250th Anniversary half dollar New York State Route 22
New York State Route 22 New York State Route 28
New York State Route 28 New York State Route 28N
New York State Route 28N New York State Route 32
New York State Route 32 New York State Route 174
New York State Route 174 New York State Route 175
New York State Route 175 New York State Route 308
New York State Route 308 New York State Route 311
New York State Route 311 Niagara Falls Suspension Bridge
Niagara Falls Suspension Bridge Oakwood Cemetery (Troy, New York)
Oakwood Cemetery (Troy, New York) 1991 Perfect Storm
1991 Perfect Storm Providence and Worcester Railroad
Providence and Worcester Railroad RKO Pictures
RKO Pictures Isidor Isaac Rabi
Isidor Isaac Rabi Riegelmann Boardwalk
Riegelmann Boardwalk Rosendale Trestle
Rosendale Trestle Rex Ryan
Rex Ryan William H. Seward
William H. Seward Elliott Fitch Shepard
Elliott Fitch Shepard Harry F. Sinclair House
Harry F. Sinclair House State Route 343 (New York−Connecticut)
State Route 343 (New York−Connecticut) New Paltz station
New Paltz station Statue of Liberty
Statue of Liberty Capture of Fort Ticonderoga
Capture of Fort Ticonderoga Harriet Tubman
Harriet Tubman Battle of Valcour Island
Battle of Valcour Island Mary van Kleeck
Mary van Kleeck Barry Voight
Barry Voight Walden–Wallkill Rail Trail
Walden–Wallkill Rail Trail P. G. Wodehouse
P. G. Wodehouse Robert Sterling Yard
Robert Sterling Yard
Featured lists
 List of highways in Warren County, New York
List of highways in Warren County, New York List of tallest buildings in New York City
List of tallest buildings in New York City List of winners of the New York City Marathon
List of winners of the New York City Marathon List of Buffalo Bills head coaches
List of Buffalo Bills head coaches List of Buffalo Sabres head coaches
List of Buffalo Sabres head coaches List of Buffalo Sabres players
List of Buffalo Sabres players List of Nobel laureates affiliated with Columbia University as alumni or faculty
List of Nobel laureates affiliated with Columbia University as alumni or faculty List of Roman Catholic archbishops of New York
List of Roman Catholic archbishops of New York List of State University of New York units
List of State University of New York units List of counties in New York
List of counties in New York Order of battle of the Battle of Long Island
Order of battle of the Battle of Long Island Lou Gehrig Memorial Award
Lou Gehrig Memorial Award List of New York hurricanes
List of New York hurricanes List of governors of New York
List of governors of New York List of presidents of New York University
List of presidents of New York University Timeline of Briarcliff Manor
Timeline of Briarcliff Manor List of international goals scored by Abby Wambach
List of international goals scored by Abby Wambach
Good articles
 2nd Canadian Regiment
2nd Canadian Regiment 10th Mountain Division (United States)
10th Mountain Division (United States) 14th Street Tunnel shutdown
14th Street Tunnel shutdown 116th Street–Columbia University station
116th Street–Columbia University station 140 Broadway
140 Broadway 270 Park Avenue (1960–2021)
270 Park Avenue (1960–2021) 370 Jay Street
370 Jay Street 750 Seventh Avenue
750 Seventh Avenue 1893 New York hurricane
1893 New York hurricane 1912–1913 Little Falls textile strike
1912–1913 Little Falls textile strike 1920 Buffalo All-Americans season
1920 Buffalo All-Americans season 1973–74 Buffalo Braves season
1973–74 Buffalo Braves season 1973 Belmont Stakes
1973 Belmont Stakes 1973 Buffalo Bills season
1973 Buffalo Bills season 1974–75 Buffalo Braves season
1974–75 Buffalo Braves season 1974–75 Buffalo Sabres season
1974–75 Buffalo Sabres season 1975–76 Buffalo Braves season
1975–76 Buffalo Braves season July 1989 Northeastern United States tornado outbreak
July 1989 Northeastern United States tornado outbreak 2000 United States Senate election in New York
2000 United States Senate election in New York 2008 NHL Winter Classic
2008 NHL Winter Classic 2010 Heluva Good! Sour Cream Dips at the Glen
2010 Heluva Good! Sour Cream Dips at the Glen 2017 New York City ePrix
2017 New York City ePrix 2018 New York City ePrix
2018 New York City ePrix 2020 New York's 22nd congressional district election
2020 New York's 22nd congressional district election Nick Abruzzese
Nick Abruzzese Curtis Aiken
Curtis Aiken Coat of arms of Albany, New York
Coat of arms of Albany, New York Albany City Hall
Albany City Hall Albany Free School
Albany Free School Albany, New York
Albany, New York Albany Pine Bush
Albany Pine Bush USS Albany (1846)
USS Albany (1846) Algonquin Hotel
Algonquin Hotel All Saints' Episcopal Church (Briarcliff Manor, New York)
All Saints' Episcopal Church (Briarcliff Manor, New York) Joseph H. Allen
Joseph H. Allen Alley Pond Park
Alley Pond Park Alma Mater (New York sculpture)
Alma Mater (New York sculpture) Amazon HQ2
Amazon HQ2 Mary Amdur
Mary Amdur American Bank Note Company Printing Plant
American Bank Note Company Printing Plant The Ansonia
The Ansonia Johnny Antonelli
Johnny Antonelli Arbor Hill Historic District–Ten Broeck Triangle
Arbor Hill Historic District–Ten Broeck Triangle Arden Valley Road
Arden Valley Road Armageddon (2008)
Armageddon (2008) Astoria Park
Astoria Park Attack on German Flatts (1778)
Attack on German Flatts (1778) Austin, Nichols and Company Warehouse
Austin, Nichols and Company Warehouse Avianca Flight 052
Avianca Flight 052 William Bliss Baker
William Bliss Baker Patricia Banks Edmiston
Patricia Banks Edmiston Barracuda Lounge
Barracuda Lounge Ed Barrow
Ed Barrow Barryville–Shohola Bridge
Barryville–Shohola Bridge Battle of Bennington
Battle of Bennington Battle of Fort Washington
Battle of Fort Washington Battle of Oriskany
Battle of Oriskany Battle of Cobleskill
Battle of Cobleskill Battle of Fort Anne
Battle of Fort Anne Battle of Harlem Heights
Battle of Harlem Heights Battle of Long Island
Battle of Long Island Battle of Setauket
Battle of Setauket Battle of Staten Island
Battle of Staten Island Battle of White Plains
Battle of White Plains Battle on Snowshoes
Battle on Snowshoes Battles of Saratoga
Battles of Saratoga Beechwood (Vanderlip mansion)
Beechwood (Vanderlip mansion) John Beilein
John Beilein Richard Coote, 1st Earl of Bellomont
Richard Coote, 1st Earl of Bellomont Ann Eliza Bleecker
Ann Eliza Bleecker Jessie Bonstelle
Jessie Bonstelle Bowery Savings Bank Building (130 Bowery)
Bowery Savings Bank Building (130 Bowery) Boxers NYC Washington Heights
Boxers NYC Washington Heights James T. Brady
James T. Brady Tawana Brawley rape allegations
Tawana Brawley rape allegations Briarcliff College
Briarcliff College Briarcliff Farms
Briarcliff Farms Briarcliff High School
Briarcliff High School Briarcliff Lodge
Briarcliff Lodge Briarcliff Manor Fire Department
Briarcliff Manor Fire Department Briarcliff Manor Public Library
Briarcliff Manor Public Library Briarcliff Manor Union Free School District
Briarcliff Manor Union Free School District Dan Brouthers
Dan Brouthers Pavel Buchnevich
Pavel Buchnevich Buffalo, New York
Buffalo, New York William Burnet (colonial administrator)
William Burnet (colonial administrator) Wellington R. Burt
Wellington R. Burt James Cagney
James Cagney Canajoharie Creek
Canajoharie Creek Candler Building (New York City)
Candler Building (New York City) Joseph A. Canning
Joseph A. Canning La Caravelle (New York City)
La Caravelle (New York City) Center Square/Hudson–Park Historic District
Center Square/Hudson–Park Historic District Central Park
Central Park Central Troy Historic District
Central Troy Historic District Ice Box Chamberlain
Ice Box Chamberlain Cherry Valley massacre
Cherry Valley massacre Shirley Chisholm
Shirley Chisholm Chittenango ovate amber snail
Chittenango ovate amber snail Francis Pharcellus Church
Francis Pharcellus Church Chyna
Chyna Rose Cleveland
Rose Cleveland Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton Eileen Collins
Eileen Collins Columbia University
Columbia University 2021–2022 Columbia University strike
2021–2022 Columbia University strike Coney Island
Coney Island John E. Corbally
John E. Corbally Patrick Corbin
Patrick Corbin Cornell Botanic Gardens
Cornell Botanic Gardens County Route 106 (Rockland County, New York)
County Route 106 (Rockland County, New York) Crowne Plaza Times Square Manhattan
Crowne Plaza Times Square Manhattan The Culinary Institute of America
The Culinary Institute of America Cushing House
Cushing House Daily News Building
Daily News Building Richard J. Daronco
Richard J. Daronco Joseph Dart
Joseph Dart Honey Davenport
Honey Davenport Bruce Davidson (equestrian)
Bruce Davidson (equestrian) Davison House
Davison House Nina Davuluri
Nina Davuluri Johnston de Peyster
Johnston de Peyster December 2013 Spuyten Duyvil derailment
December 2013 Spuyten Duyvil derailment Murder of Bianca Devins
Murder of Bianca Devins William J. Devlin
William J. Devlin Robert Dirks
Robert Dirks Dongan Charter
Dongan Charter Alphonsus J. Donlon
Alphonsus J. Donlon Downtown Ossining Historic District
Downtown Ossining Historic District Dr. Holbrook's Military School
Dr. Holbrook's Military School Crystal Dunn
Crystal Dunn E (New York City Subway service)
E (New York City Subway service) East Side Access
East Side Access Eastern Air Lines Flight 663
Eastern Air Lines Flight 663 Edward M. Cotter (fireboat)
Edward M. Cotter (fireboat) Effects of Hurricane Isabel in New York and New England
Effects of Hurricane Isabel in New York and New England Eighth Grade (film)
Eighth Grade (film) Electric Company (football)
Electric Company (football) Ely Hall
Ely Hall William J. Ennis
William J. Ennis Entranceway at Main Street at Roycroft Boulevard
Entranceway at Main Street at Roycroft Boulevard Entranceways at Main Street at Lamarck Drive and Smallwood Drive
Entranceways at Main Street at Lamarck Drive and Smallwood Drive Esopus Creek
Esopus Creek Ethan Allen Express
Ethan Allen Express Arthur Eve
Arthur Eve Johnny Evers
Johnny Evers Thomas Farrell (United States Army officer)
Thomas Farrell (United States Army officer) Felix M. Warburg House
Felix M. Warburg House Fellows v. Blacksmith
Fellows v. Blacksmith Bob Ferguson (infielder)
Bob Ferguson (infielder) Geraldine Ferraro
Geraldine Ferraro Tina Fey
Tina Fey Abigail Fillmore
Abigail Fillmore First American International Road Race
First American International Road Race Hamilton Fish
Hamilton Fish Val Logsdon Fitch
Val Logsdon Fitch Floyd Bennett Field
Floyd Bennett Field Flushing Meadows–Corona Park
Flushing Meadows–Corona Park Jerry Fodor
Jerry Fodor Fonteyn Kill
Fonteyn Kill Siege of Fort Ticonderoga (1777)
Siege of Fort Ticonderoga (1777) Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery
Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery Four Seasons Restaurant
Four Seasons Restaurant James Franco
James Franco The French Connection (ice hockey)
The French Connection (ice hockey) Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman Frontier Central School District
Frontier Central School District Klaus Fuchs
Klaus Fuchs Kirsten Gillibrand
Kirsten Gillibrand Ruth Bader Ginsburg
Ruth Bader Ginsburg Glenwood Generating Station
Glenwood Generating Station Maria Goeppert Mayer
Maria Goeppert Mayer Golos Truda
Golos Truda Dennis Gorski
Dennis Gorski Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould Grand Central Terminal
Grand Central Terminal Mike Gravel
Mike Gravel Mallory Hagan
Mallory Hagan Ray Hall (basketball)
Ray Hall (basketball) Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton William S. Hamilton
William S. Hamilton Edward A. Hanna
Edward A. Hanna Harriman station (Erie Railroad)
Harriman station (Erie Railroad) Abram Lincoln Harris
Abram Lincoln Harris Hart Island
Hart Island Joseph Hazelwood
Joseph Hazelwood Heckscher State Parkway
Heckscher State Parkway Helmsley Building
Helmsley Building Lorena Hickok
Lorena Hickok Lauryn Hill
Lauryn Hill Joseph J. Himmel
Joseph J. Himmel History of Cornell University
History of Cornell University History of Briarcliff Manor
History of Briarcliff Manor Hotel McAlpin
Hotel McAlpin Louis Howe
Louis Howe Hudson River
Hudson River Huletts Landing, New York
Huletts Landing, New York Shane Hurlbut
Shane Hurlbut Tillinghast L'Hommedieu Huston
Tillinghast L'Hommedieu Huston Hutchinson River Parkway
Hutchinson River Parkway Hyatt Grand Central New York
Hyatt Grand Central New York In Your House 1
In Your House 1 Independent Democratic Conference
Independent Democratic Conference Industry Bar
Industry Bar Interstate 87 (New York)
Interstate 87 (New York) Interstate 190 (New York)
Interstate 190 (New York) Interstate 287
Interstate 287 Invasion of Quebec (1775)
Invasion of Quebec (1775) The Irishman
The Irishman Washington Irving
Washington Irving Caitlyn Jenner
Caitlyn Jenner Jewett House
Jewett House George McTurnan Kahin
George McTurnan Kahin Jack Kemp
Jack Kemp PS Keystone State
PS Keystone State Joyce Kilmer
Joyce Kilmer Landing at Kip's Bay
Landing at Kip's Bay Kissena Creek
Kissena Creek Knife Edge Two Piece 1962–65
Knife Edge Two Piece 1962–65 Seymour H. Knox I
Seymour H. Knox I Harold Kushner
Harold Kushner Lafayette Park Historic District
Lafayette Park Historic District Lafayette Square (Buffalo, New York)
Lafayette Square (Buffalo, New York) Lake Ontario Ordnance Works
Lake Ontario Ordnance Works Lathrop House (Vassar College)
Lathrop House (Vassar College) Walter W. Law
Walter W. Law Lexington Hotel (New York City)
Lexington Hotel (New York City) Ryan Lochte
Ryan Lochte Loop Parkway
Loop Parkway Sid Luckman
Sid Luckman Lucky and Squash
Lucky and Squash John Van Antwerp MacMurray
John Van Antwerp MacMurray Sal Maglie
Sal Maglie Sean Patrick Maloney
Sean Patrick Maloney Sandro Mamukelashvili
Sandro Mamukelashvili Manhattan House
Manhattan House Manhattan
Manhattan Marcellus Formation
Marcellus Formation Nancy Marcus
Nancy Marcus James C. Marshall
James C. Marshall Ashley Massaro
Ashley Massaro Massena Terminal Railroad
Massena Terminal Railroad Jack F. Matlock Jr.
Jack F. Matlock Jr. Steven Matz
Steven Matz Mary Arthur McElroy
Mary Arthur McElroy Jason McElwain
Jason McElwain Priscilla Johnson McMillan
Priscilla Johnson McMillan Meadowbrook State Parkway
Meadowbrook State Parkway Meigs Raid
Meigs Raid SS Merchant
SS Merchant Metropolitan Life Insurance Company Tower
Metropolitan Life Insurance Company Tower Millennium Times Square New York
Millennium Times Square New York Mirabito Outdoor Classic
Mirabito Outdoor Classic Montauk Point land claim
Montauk Point land claim Grandma Moses
Grandma Moses Mark Murphy (American football executive)
Mark Murphy (American football executive) Michael P. Murphy
Michael P. Murphy Joe Nathan
Joe Nathan IRT New Lots Line
IRT New Lots Line New York and New Jersey campaign
New York and New Jersey campaign USS New York (BB-34)
USS New York (BB-34) New York Biltmore Hotel
New York Biltmore Hotel New York Court of Appeals Building
New York Court of Appeals Building New York Jets
New York Jets New York Public Library Main Branch
New York Public Library Main Branch New York State Route 5
New York State Route 5 New York State Route 7
New York State Route 7 New York State Route 9A
New York State Route 9A New York State Route 20SY
New York State Route 20SY New York State Route 23
New York State Route 23 New York State Route 28A
New York State Route 28A New York State Route 31
New York State Route 31 New York State Route 43
New York State Route 43 New York State Route 45
New York State Route 45 New York State Route 59
New York State Route 59 New York State Route 78
New York State Route 78 New York State Route 92
New York State Route 92 New York State Route 101
New York State Route 101 New York State Route 108
New York State Route 108 New York State Route 111
New York State Route 111 New York State Route 114
New York State Route 114 New York State Route 117
New York State Route 117 New York State Route 118
New York State Route 118 New York State Route 120A
New York State Route 120A New York State Route 120
New York State Route 120 New York State Route 128
New York State Route 128 New York State Route 129
New York State Route 129 New York State Route 132
New York State Route 132 New York State Route 134
New York State Route 134 New York State Route 141
New York State Route 141 New York State Route 146
New York State Route 146 New York State Route 164
New York State Route 164 New York State Route 173
New York State Route 173 New York State Route 210
New York State Route 210 New York State Route 216
New York State Route 216 New York State Route 217
New York State Route 217 New York State Route 284
New York State Route 284 New York State Route 292
New York State Route 292 New York State Route 293
New York State Route 293 New York State Route 306
New York State Route 306 New York State Route 312
New York State Route 312 New York State Route 335
New York State Route 335 New York State Route 344
New York State Route 344 New York State Route 361
New York State Route 361 New York State Route 375
New York State Route 375 New York State Route 376
New York State Route 376 New York State Route 402
New York State Route 402 New York State Route 448
New York State Route 448 New York State Route 598
New York State Route 598 New York State Route 878
New York State Route 878 New York Yankees
New York Yankees New York-class battleship
New York-class battleship Newburgh, Dutchess and Connecticut Railroad
Newburgh, Dutchess and Connecticut Railroad Francis Nicholson
Francis Nicholson Joe Nieuwendyk
Joe Nieuwendyk Noble train of artillery
Noble train of artillery North Shore Towers
North Shore Towers Not My Presidents Day
Not My Presidents Day Leo J. O'Donovan
Leo J. O'Donovan Arthur A. O'Leary
Arthur A. O'Leary Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez
Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez County of Oneida v. Oneida Indian Nation of New York State
County of Oneida v. Oneida Indian Nation of New York State Peter Ostrum
Peter Ostrum The Other Woman (2014 film)
The Other Woman (2014 film) Otsego Lake (New York)
Otsego Lake (New York) Our Lady of Pompeii Church (Manhattan)
Our Lady of Pompeii Church (Manhattan) Palisades Interstate Parkway
Palisades Interstate Parkway Park Avenue Armory
Park Avenue Armory Alton B. Parker
Alton B. Parker George N. Parks
George N. Parks Henry B. Payne
Henry B. Payne The Peninsula New York
The Peninsula New York Gilbert Perreault
Gilbert Perreault The Philaletheis Society
The Philaletheis Society The Place Beyond the Pines
The Place Beyond the Pines Pompey stone
Pompey stone Pond Eddy Bridge
Pond Eddy Bridge Port of Albany–Rensselaer
Port of Albany–Rensselaer Natalie Portman
Natalie Portman Loretta Preska
Loretta Preska Publishers Clearing House
Publishers Clearing House Q35 (New York City bus)
Q35 (New York City bus) Raid on Unadilla and Onaquaga
Raid on Unadilla and Onaquaga James Rainwater
James Rainwater Norman Ramsey Jr.
Norman Ramsey Jr. Keith Raniere
Keith Raniere Vic Raschi
Vic Raschi Rector v. Major League Baseball Advanced Media
Rector v. Major League Baseball Advanced Media Kiliaen van Rensselaer (merchant)
Kiliaen van Rensselaer (merchant) Richmond Hill station (LIRR)
Richmond Hill station (LIRR) Dick Rifenburg
Dick Rifenburg John D. Rockefeller
John D. Rockefeller Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt Rosendale (CDP), New York
Rosendale (CDP), New York Rosendale Theatre
Rosendale Theatre Murray Rothbard
Murray Rothbard Lester Rowe
Lester Rowe Nicholas Russo
Nicholas Russo Sagtikos State Parkway
Sagtikos State Parkway Edward Said
Edward Said St. Mary's Church (Albany, New York)
St. Mary's Church (Albany, New York) St. Mary's-in-Tuxedo Episcopal Church
St. Mary's-in-Tuxedo Episcopal Church St. Patrick's Cathedral (Midtown Manhattan)
St. Patrick's Cathedral (Midtown Manhattan) St. Regis New York
St. Regis New York Salt (2010 film)
Salt (2010 film) Savanna Samson
Savanna Samson Jedediah Sanger
Jedediah Sanger Saratoga campaign
Saratoga campaign Peter Sarsgaard
Peter Sarsgaard Linda Sarsour
Linda Sarsour Richard Henry Savage
Richard Henry Savage Marilyn Saviola
Marilyn Saviola Saw Mill River
Saw Mill River Scarborough Day School
Scarborough Day School Scarborough Historic District
Scarborough Historic District Scarborough station (Metro-North)
Scarborough station (Metro-North) Norman Schwarzkopf Jr.
Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. Seeley G. Mudd Chemistry Building
Seeley G. Mudd Chemistry Building Seneca Falls Convention
Seneca Falls Convention Seneca Nation of Indians v. Christy
Seneca Nation of Indians v. Christy Cy Seymour
Cy Seymour Whitney North Seymour Jr.
Whitney North Seymour Jr. Siege of Fort Stanwix
Siege of Fort Stanwix Siege of Fort William Henry
Siege of Fort William Henry Skinners Falls–Milanville Bridge
Skinners Falls–Milanville Bridge Sleepy Hollow Country Club
Sleepy Hollow Country Club Sloatsburg station
Sloatsburg station Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Battle on Snowshoes (1757)
Battle on Snowshoes (1757) Snyder, New York
Snyder, New York Sonia Sotomayor
Sonia Sotomayor South End–Groesbeckville Historic District
South End–Groesbeckville Historic District Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Elizabeth Cady Stanton State Route 346 (New York–Vermont)
State Route 346 (New York–Vermont) Staten Island Peace Conference
Staten Island Peace Conference Statue of James S. T. Stranahan
Statue of James S. T. Stranahan Stork Club
Stork Club Students' Building (Vassar College)
Students' Building (Vassar College) Syracuse University Alma Mater
Syracuse University Alma Mater Syracuse University
Syracuse University Martin F. Tanahey
Martin F. Tanahey Henry Taube
Henry Taube Telluride House
Telluride House Tesla, Inc.
Tesla, Inc. Al Thake
Al Thake Therapy (New York City)
Therapy (New York City) Third Onondaga County courthouse
Third Onondaga County courthouse Antoine Thompson
Antoine Thompson Obi Toppin
Obi Toppin Trump National Golf Club Westchester
Trump National Golf Club Westchester Taro Tsujimoto
Taro Tsujimoto U.S. Route 4 in New York
U.S. Route 4 in New York Underground World Home
Underground World Home Unisphere
Unisphere United Rentals 176 at The Glen
United Rentals 176 at The Glen United States v. McMahon
United States v. McMahon Harold Urey
Harold Urey Utica, New York
Utica, New York Valhalla train crash
Valhalla train crash The View (talk show)
The View (talk show) William Vitarelli
William Vitarelli Marquise Walker
Marquise Walker Wallkill Valley Rail Trail
Wallkill Valley Rail Trail Nina de Creeft Ward
Nina de Creeft Ward Pop Warner
Pop Warner PS Washington Irving
PS Washington Irving Washington Park Historic District (Albany, New York)
Washington Park Historic District (Albany, New York) Max Weinberg
Max Weinberg Murder of Peter Weinberger
Murder of Peter Weinberger West Kill
West Kill Jamaal Westerman
Jamaal Westerman Elmer White
Elmer White Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman John Wieting
John Wieting Wieting Opera House
Wieting Opera House WNYO-TV
WNYO-TV The Wolf of Wall Street (2013 film)
The Wolf of Wall Street (2013 film) Woodstock 50
Woodstock 50 Woolworth Building
Woolworth Building Chien-Shiung Wu
Chien-Shiung Wu
Related portals
State facts
- Nicknames: The Empire State, The Excelsior State
- Capital: Albany
- Governor: Andrew Cuomo (D)
- Lieutenant Governor: Kathy Hochul (D)
- Secretary of State: Rossana Rosado (D)
- Attorney General: Letitia James (D)
- Total area: 54,555 mi2
- Land: 47,190 mi2
- Water: 7,365 mi2
- Highest elevation: 5,344 ft (Mount Marcy)
- Population 19,745,289 (2016 est)
- Admission to the Union: July 26, 1788 (11th)
State symbols:
- Animal: Beaver
- Bird: Eastern Bluebird
- Colors: Blue & Gold
- Freshwater Fish: Brook trout
- Saltwater Fish: Striped bass
- Flower: Rose
- Fossil: Eurypterus remipes
- Insect: Nine-spotted Ladybug
- Songs: "I Love New York"
- Tree: Sugar Maple
- Gem: Garnet
WikiProjects
- Main project
- New York State
- Regional
- Capital District
- Hudson Valley
- Long Island
- New York City
- Syracuse
- Western New York
- Specific topics
- Columbia University
- Cornell University
- State University of New York
Things you can do

- Requested articles: Hinduism in New York
- Help assess articles supported by WikiProject New York (state)
- Help suggest content for usage in this portal by using the archive links to obtain instructions
- Write New York topics if you see a redlink which is worthy of an article
- Cleanup and expand stub-class articles relating to New York
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals























.svg.png.webp)