The Cities Portal

A city is a human settlement of a notable size. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organizations, and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving the efficiency of goods and service distribution.
Historically, city dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for global sustainability. Present-day cities usually form the core of larger metropolitan areas and urban areas—creating numerous commuters traveling toward city centres for employment, entertainment, and education. However, in a world of intensifying globalization, all cities are to varying degrees also connected globally beyond these regions. This increased influence means that cities also have significant influences on global issues, such as sustainable development, climate change, and global health. Because of these major influences on global issues, the international community has prioritized investment in sustainable cities through Sustainable Development Goal 11. Due to the efficiency of transportation and the smaller land consumption, dense cities hold the potential to have a smaller ecological footprint per inhabitant than more sparsely populated areas. Therefore, compact cities are often referred to as a crucial element in fighting climate change. However, this concentration can also have significant negative consequences, such as forming urban heat islands, concentrating pollution, and stressing water supplies and other resources. (Full article...)
Selected city -
Pompeii (/pɒmˈpeɪ(i)/ pom-PAY-(ee), Latin: [pɔmˈpei̯.iː]) was an ancient city located in what is now the comune of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under 4 to 6 m (13 to 20 ft) of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.
Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offers a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost because of excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found could be used as moulds to make plaster casts of unique, and often gruesome, figures in their final moments of life. The numerous graffiti carved on the walls and inside rooms provide a wealth of examples of the largely lost Vulgar Latin spoken colloquially at the time, contrasting with the formal language of the classical writers. (Full article...)Did you know -
- ... that the "awkward, cramped galleries" at 2 Columbus Circle later housed New York City government offices?
- ... that the 1971 Hazelwood massacre was the largest mass murder in the history of "Murder City"?
- ... that Ashton Hawkins arranged for the construction of the West Wing of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, to house the Temple of Dendur?
- ... that it took almost as long to renovate New York City's Borough Hall station in the 1980s as it did to construct the original subway line?
- ... that only about a quarter of New York City's 472 subway stations had elevators in 2018, among the lowest accessibility rates of the world's major transit systems?
- ... that Swansea City made two appearances at the Millennium Stadium in 2006, winning the Football League Trophy but losing the Football League One play-off Final?
Related portals
Related WikiProjects
![]()
- WikiProject Cities
- WikiProject Countries
- WikiProject Geography
 Recognized content -
Recognized content - 
Albany (/ˈɔːlbəni/ ⓘ AWL-bən-ee) is the capital city of the U.S. state of New York and the seat of Albany County. It is located on the west bank of the Hudson River, about 10 miles (16 km) south of its confluence with the Mohawk River, and about 135 miles (220 km) north of New York City.
The city is known for its architecture, commerce, culture, institutions of higher education, and rich history. It is the economic and cultural core of the Capital District of the State of New York, which comprises the Albany–Schenectady–Troy Metropolitan Statistical Area, including the nearby cities and suburbs of Troy, Schenectady, and Saratoga Springs. With an estimated population of 1.1 million in 2013, the Capital District is the third most populous metropolitan region in the state. As of 2020, Albany's population was 99,224. (Full article...)Selected article -
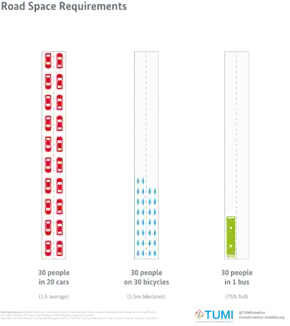
The compact city or city of short distances is an urban planning and urban design concept, which promotes relatively high residential density with mixed land uses. It is based on an efficient public transport system and has an urban layout which – according to its advocates – encourages walking and cycling, low energy consumption and reduced pollution. A large resident population provides opportunities for social interaction as well as a feeling of safety in numbers and "eyes on the street". It is also arguably a more sustainable urban settlement type than urban sprawl because it is less dependent on the car, requiring less (and cheaper per capita) infrastructure provision (Williams 2000, cited in Dempsey 2010).
Achieving a compact city does not just mean increasing urban density per se or across all parts of the city. It means good planning to achieve an overall more compact urban form:
The compact city model, ideally, creates benefits that are attractive to modern urbanites. The desired benefits include shorter commute times, reduced environmental impact of the community, and reduced consumption of fossil fuels and energy. However, research on compact cities from around the globe suggests that these outcomes are not guaranteed. To make matters worse, the design of the cities is limiting residents’ access to green space and reasonable views. For the compact city model to gain in popularity, it is necessary to review both their pros and cons. (Full article...)Governments of sprawling cities can take many actions to seek a more compact form, often also involving higher densities. Other cities, such as Cairo, with large, dense slum areas, are responding by reducing urban densities in core areas. In either case, limiting outward urban expansion can be combined with more efficient use of land resources and more effective protection of natural resources. City growth can be physically limited in this way through legislated urban growth boundaries, non-urban green belts, and the quarantining of development in certain areas.
General images -
Topics
List articles
Subcategories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals






.jpg.webp)








_LACMA_M.2008.40.98.8.jpg.webp)