The 1920s PortalThe 1920s (pronounced "nineteen-twenties" often shortened to the "'20s" or the "Twenties") was a decade that began on January 1, 1920, and ended on December 31, 1929. In America, it is frequently referred to as the "Roaring Twenties" or the "Jazz Age", while in Europe the period is sometimes referred to as the "Golden Twenties" because of the economic boom following World War I (1914–1918). French speakers refer to the period as the "Années folles" ("crazy years"), emphasizing the era's social, artistic, and cultural dynamism.
Silent films were popular in this decade, with the highest-grossing film of this decade being either the American silent epic adventure-drama film Ben-Hur: A Tale of the Christ or the American silent war drama film The Big Parade, depending on the metrics used. Sinclair Lewis was a popular author in the United States in the 1920s, with his books Main Street and Elmer Gantry becoming best-sellers. Best-selling books outside the US included the Czech book The Good Soldier Švejk, which sold 20 million copies. Songs of this decade included "Mack the Knife" and "Tiptoe Through the Tulips". During the 1920s, the world population increased from 1.87 to 2.05 billion, with approximately 700 million births and 525 million deaths in total. (Full article...) Selected article - A 1919 parade in Washington, D.C. for soldiers returning home after World War I. The upheaval associated with the transition from a wartime to peacetime economy contributed to a depression in 1920 and 1921. The Depression of 1920–1921 was a sharp deflationary recession in the United States, United Kingdom and other countries, beginning 14 months after the end of World War I. It lasted from January 1920 to July 1921. The extent of the deflation was not only large, but large relative to the accompanying decline in real product. There was a two-year post–World War I recession immediately following the end of the war, complicating the absorption of millions of veterans into the economy. The economy started to grow, but it had not yet completed all the adjustments in shifting from a wartime to a peacetime economy. Factors identified as contributing to the downturn include returning troops, which created a surge in the civilian labor force and problems in absorbing the veterans; Spanish flu; a decline in labor union strife; changes in fiscal and monetary policy; and changes in price expectations. (Full article...)Featured picture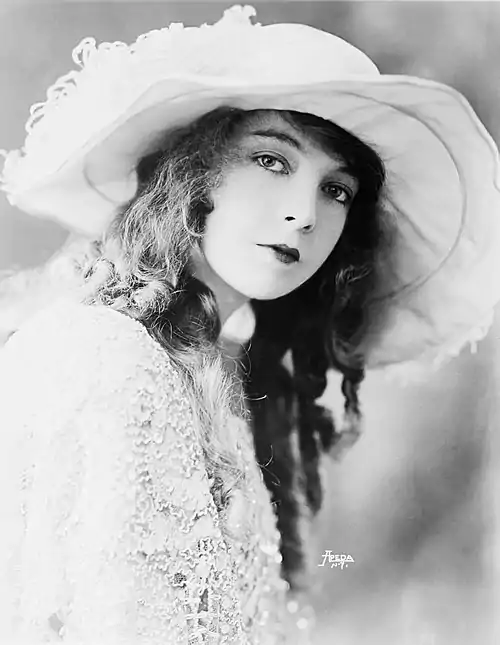 Lillian Gish A portrait of Lillian Gish from 1921. Gish was one of the first female movie stars, called "The First Lady of American Cinema", starting in 1912 and continuing to appear in films until 1987. The American Film Institute named Gish 17th among the greatest female stars of all time and awarded her a Life Achievement Award, making her the only recipient who was a major figure in the silent era. Remarkably, she never won an Academy Award for her work, although she did receive a Special Academy Award in 1971. Did you know...
Related portalsSelected biography -William Randolph Hearst Sr. (/hɜːrst/; April 29, 1863 – August 14, 1951) was an American businessman, newspaper publisher, and politician known for developing the nation's largest newspaper chain and media company, Hearst Communications. His flamboyant methods of yellow journalism influenced the nation's popular media by emphasizing sensationalism and human interest stories. Hearst entered the publishing business in 1887 with Mitchell Trubitt after being given control of The San Francisco Examiner by his wealthy father, Senator George Hearst. After moving to New York City, Hearst acquired the New York Journal and fought a bitter circulation war with Joseph Pulitzer's New York World. Hearst sold papers by printing giant headlines over lurid stories featuring crime, corruption, sex, and innuendos. Hearst acquired more newspapers and created a chain that numbered nearly 30 papers in major American cities at its peak. He later expanded to magazines, creating the largest newspaper and magazine business in the world. Hearst controlled the editorial positions and coverage of political news in all his papers and magazines, and thereby often published his personal views. He sensationalized Spanish atrocities in Cuba while calling for war in 1898 against Spain. Historians, however, reject his subsequent claims to have started the war with Spain as overly extravagant. (Full article...)TopicsWikiProjects
List articlesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
1920s-related lists 1920-related lists 1921-related lists 1922-related lists 1923-related lists 1924-related lists 1925-related lists 1926-related lists 1927-related lists 1928-related lists 1929-related lists Lists of 1920s films 1920s politics-related lists More Did you know (auto generated)
Categories 1920s 1920 1921 1922 1923 1924 1925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1920s by city 1920s by continent 1920s by country 1920s-related lists Months in the 1920s 1920s beginnings 1920s endings 1920s decade overviews 1920s in LGBT history 1920s in philosophy 1920s meteorology 1920s missing person cases 1920s architecture 1920s in the arts 1920s awards 1920s censuses 1920s competitions 1920s conferences 1920s disasters 1920s economic history 1920s in education 1920s in the environment 1920s events 1920s fads and trends 1920s fashion 1920s festivals Fiction set in the 1920s 1920s in film 1920s in health 1920s hoaxes Interwar period 1920s in law 1920s in mass media 1920s in military history 1920s in politics 1920s in religion 1920s in science 1920s in sports 1920s in technology 1920s toys 1920s in transport 1920s in women's history 1920s works General imagesThe following are images from various 1920s-related articles on Wikipedia.
Recognized contentFeatured articles:
Featured lists: Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|



_(cropped).jpg.webp)


_Cropped.jpg.webp)










.jpg.webp)

.svg.png.webp)
_-_Fondo_Mar%C3%ADn-Kutxa_Fototeka.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)


_-_2.JPG.webp)