 | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,2-diamine | |||
| Other names
o-Phenylene diamine 1,2-Diaminobenzene 1,2-Phenylenediamine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.210 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1673 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H8N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 108.144 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.031 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 102 to 104 °C (216 to 219 °F; 375 to 377 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 252 °C (486 °F; 525 K) Other sources: 256 to 258 °C (493 to 496 °F; 529 to 531 K) | ||
| soluble in hot water | |||
| Acidity (pKa) |
| ||
| -71.98·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
    | |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H312, H317, H319, H332, H341, H351, H410 | |||
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+P313, P337+P313, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 156 °C (313 °F; 429 K) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
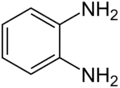
O-phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. It is isomeric with m-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine.
Preparation
Commonly, 2-nitrochlorobenzene is treated with ammonia and the resulting 2-nitroaniline, whose nitro group is then reduced:[4]
- ClC6H4NO2 + 2 NH3 → H2NC6H4NO2 + NH4Cl
- H2NC6H4NO2 + 3 H2 → H2NC6H4NH2 + 2 H2O
In the laboratory, the reduction of the nitroaniline is effected with zinc powder in ethanol, followed by purification of the diamine as the hydrochloride salt.[5] This compound darkens upon exposure to air. Sodium dithionite and activated carbon are utilized to purify a hot aqueous solution. The solution is then cooled and crystallized to remove impurities.
Reactions and uses
o-Phenylenediamine condenses with ketones and aldehydes to give rise to various valuable products. Its reactions with carboxylic acids and their derivatives produce benzimidazoles. The herbicides benomyl and fuberidazole are made in this manner. Thiophanate-methyl is another herbicide produced from o-phenylenediamine.[4]
Quinoxalinedione may be prepared by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with dimethyl oxalate. Mercaptoimidazole are commonly used as antioxidants in rubber production, obtained by condensing xanthate esters. Treatment with nitrous acid gives benzotriazole, a corrosion inhibitor. Condensation of substituted o-phenylenediamine with diketones yields various pharmaceuticals.[6]
Phenylenediamine is a significant precursor of ligands in coordination chemistry. Schiff base derivatives, such as those derived from salicylaldehyde, are excellent chelating ligands. Oxidation of its metal-phenylenediamine complexes affords the diimine derivatives, which are intensely colored and often exist in multiple stable oxidation states.[7]
Safety
With an LD50 of 44 mg/L (in water), o-phenylenediamine is about 1000 times less toxic than the para-isomer. Anilines are typically handled as if they are carcinogenic. For many applications, OPD has been replaced by safer alternatives such as 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine.[8]
References
- ↑ "DuPont Specialty Intermediates: o-Phenylenediamine (OPD)". Archived from the original on June 22, 2008. Retrieved April 25, 2006.
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 5–89. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ↑ "Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) : 2893 - PubChem". PubChem.
- 1 2 Smiley, Robert A. (2000). "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_405.
- ↑ E. L. Martin (1939). "o-Phenylenediamine". Organic Syntheses. 19: 70. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.019.0070. Archived from the original on March 2, 2022.
- ↑ See for example, Renault, J.; et al. (1981). "Heterocyclic quinones. Quinoxaline-5,6 and 5,8 diones, potential antitumoral agents". Eur. J. Med. Chem. 16: 545–550.
- ↑ Warren, L. F. (1977). "Synthesis of [M'-N4] and [M'-N6] Complexes Based on o-Benzoquinone Diimine with Cobalt, Iron, and Ruthenium". Inorg. Chem. 16 (11): 2814–2819. doi:10.1021/ic50177a028.
- ↑ Deshpande SS (1996). Enzyme Immunoassays: From Concept to Product Development. New York: Chapman & Hall. p. 169. ISBN 978-0-412-05601-7.